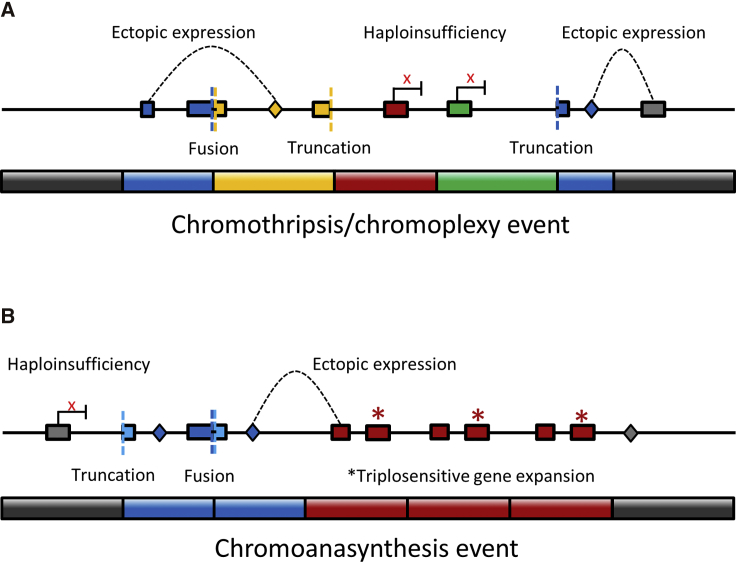
Figure 3.
Functional Consequences of Chromoanagenesis
Rearranged chromosome fragments are colored in blue, yellow, red, and green. Grey fragments represent the remainder of the chromosome, to pter (left gray fragments) and qter (right gray fragment).
(A) Chromothripsis/chromoplexy events can lead to gene truncation (colored boxes and colored dashed lines), fusions (adjacent colored boxes and colored dashed lines), gene haploinsufficiency due to removal of regulatory elements (enhancers marked as colored diamonds and haploinsufficient gene transcription marked with an x), or ectopic expression caused by position effects (enhancers marked as colored diamonds and dashed lines indicate the genes on which they are exerting their effects).
(B) Similar to chromothripsis/chromoplexy, chromoanasynthesis can lead to gene truncation, gene fusion, gene haploinsufficiency due to removal of regulatory elements or ectopic expression. In addition, expansion and transcription of triplosensitive genes could be observed in chromoanasynthesis.