Figure 3.
Functional In Vitro and In Vivo Studies of Truncated UBAP1
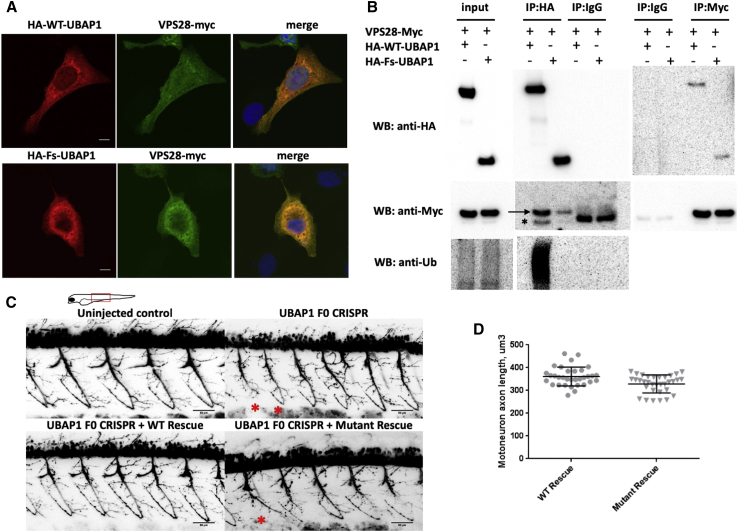
(A) Immunostaining of U2OS cells transfected with HA-WT-UBAP1 HA-Fs-UBAP1 (p.Leu121Profs∗18) and VPS-28-Myc. Both wild-type and mutant UBAP1 co-localize with VPS28-Myc.
(B) A co-immunoprecipitation assay shows protein-protein interaction between VPS28-Myc and both HA-WT-UBAP1 and HA-Fs-UBAP1. Ubiquitinated proteins co-immunoprecipitated with HA-WT-UBAP1 but not with HA-Fs-UBAP1. The arrow points to VPS28-Myc, and the asterisk bellow the arrow indicates the IgG band.
(C) Motor-neuron axons in Tg(olig2∷DsRed) zebrafish embryos at 48 hpf. Embryos were injected with CRISPR Cas9 and sgRNAs against UBAP1; injection was supplemented with human RNA rescue of wild-type or truncated mutant UBAP1. Truncated and misshaped axons were more commonly observed with mutant hRNA rescue (indicated by asterisks). Scale bars represent 50 μm. The phenotypic difference between treated groups was evaluated by a Fisher exact test. Samples were assigned to either normal or affected categories on the basis of the presence of truncated and misshaped axons. The Fisher exact statistic value was determined to be 0.003; the result is significant at p < 0.005. Statistics describing normal versus affected phenotypes were calculated on the basis of the following sample sizes (number of embryos observed as having a phenotype). F0 CRISPR + wild-type hRNA rescue: normal = 11, affected = 1. F0 CRISPR + mutant hRNA rescue (family 4, p.Leu121Profs∗18), normal = 9, affected = 15.
(D) Quantification of the individual motor-axon lengths. p values were calculated with a one-tailed Student’s t test.: p = 0.0008 and n = 9 (number of embryos in each experimental group; four axons were measured per embryo).