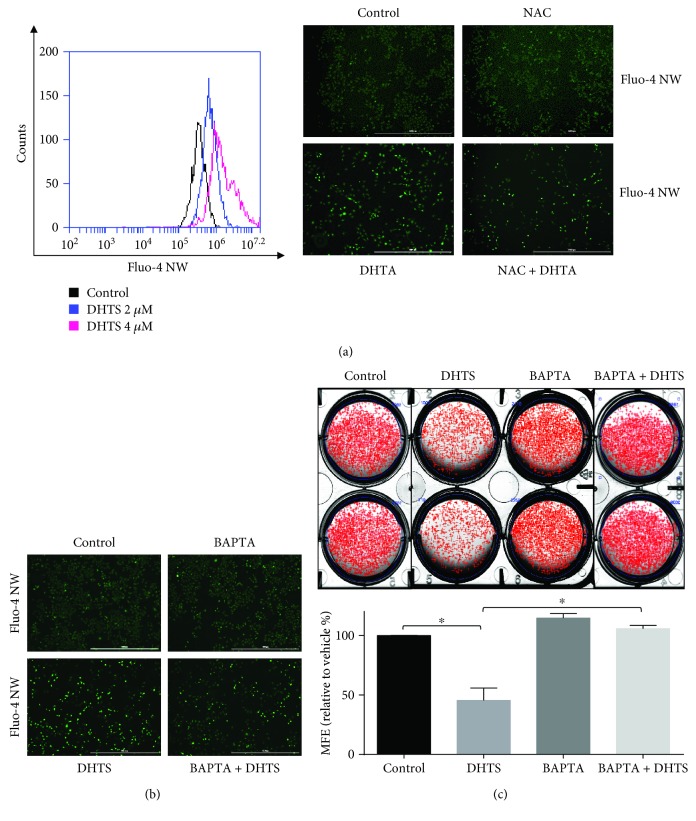
Figure 6.
DHTS triggers CSC death by increasing calcium release. DHTS induced calcium release, and DHTS-induced calcium release was ameliorated by NAC. Breast cancer cells were treated with 2 and 4 μM DHTS, and calcium release was assayed using a calcium assay kit containing Fluo-4 AW reagent. After DHTS treatment, cancer cells were stained with Fluo-4 AW, and calcium release was detected by fluorescence microscopy (4x) (scale bar = 1000 μm) (a). DHTS induced calcium release, and DHTS-induced calcium release was ameliorated by the calcium chelator BAPTA. Breast cancer cells were treated with DHTS with/without BAPTA, cancer cells were stained with Fluo-4 AW, and calcium release was detected by fluorescence microscopy (4x) (scale bar = 1000 μm) (b). DHTS-induced calcium release inhibited CSC formation, and its inhibition was ameliorated by a calcium chelator. The dissociated MDA-231-MB cells were seeded in 6-well plates on CSC media and treated with the indicated concentrations of DHTS and BAPTA for 7 days. Representative images of colonies were recorded. The data shown represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05 vs. the DMSO-treated control (c).