Figure 3.
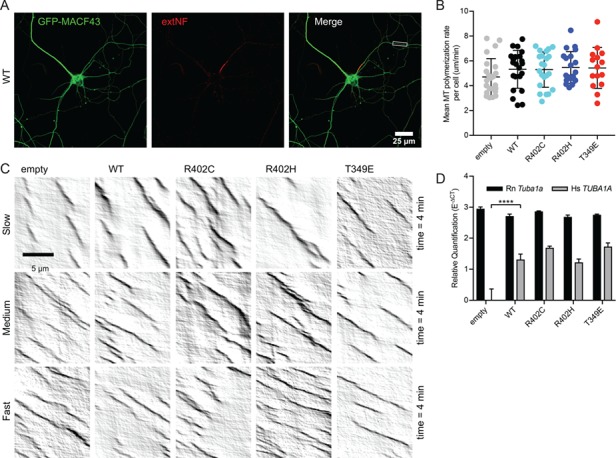
Ectopic expression of TUBA1A mutant alleles is not sufficient to disrupt axonal microtubule polymerization in primary neuronal culture. (A) Representative image of DIV11 primary rat cortical neuron expressing pCIG2-Tuba1a(WT)-ires-GFP-MACF43 and live-stained with extNF to reveal AIS. Inset reveals axonal segment selected for kymograph analysis. (B) Microtubule polymerization rate. Each data point represents cellular mean microtubule polymerization rate, with bars displaying mean ± SEM. No significant differences to empty vector or WT control, with significance determined as P < 0.05. (C) Representative kymographs from each condition displaying variation in microtubule polymerization rates observed across cells. (D) Relative quantification of endogenous, rat Tuba1a (Rn Tuba1a) and ectopic, human TUBA1A (Hs TUBA1A) mRNA levels using RT-qPCR on RNA isolated from GFP-positive neuron population after FACS. Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation. Quadruple asterisks indicate significant difference compared to WT, by t-test (P < 0.0001).
