Figure 2.
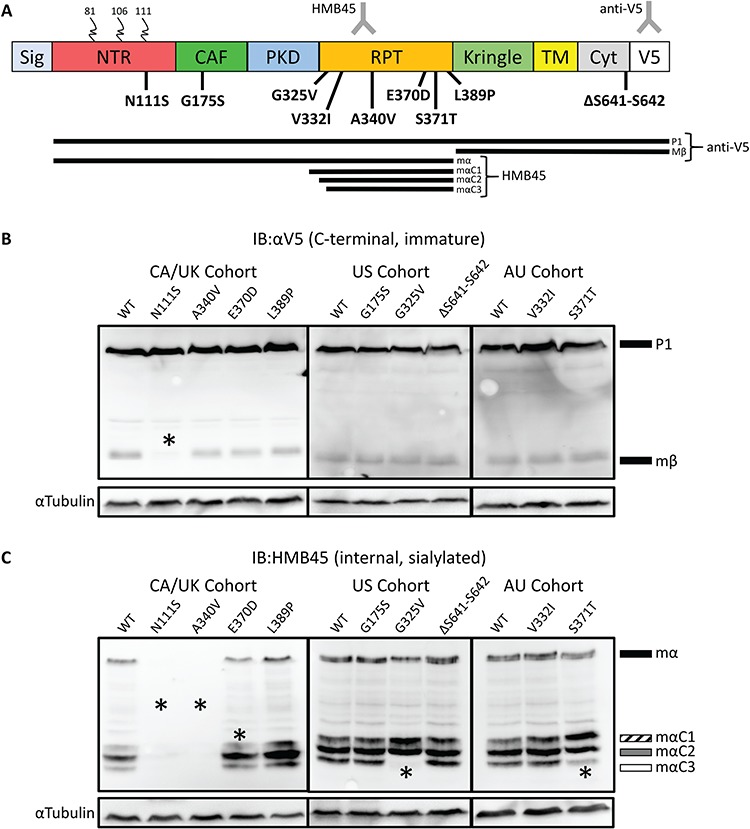
Processing defects apparent in PMEL patient variants. (A) Schematic representation of PMEL protein, the patient variants reported here, and PMEL processing intermediates. Colored blocks indicate protein domains. Curled lines indicate N-linked glycosylation. Sig, Signal domain; NTR, CAF, PKD, RPT, Kringle, Kringle-like Domain; TM, transmembrane domain; Cyt, cytoplasmic domain; V5, V5 tag. The bottom of panel A presents processing intermediates detected by IB, including the C-terminal anti-V5 and internal sialylation specific HMB45 antibodies. The lines represent intermediate processing forms detected by the different antibodies. The HMB45 antibody binds in the RPT domain and is specific to mature sialylated PMEL while anti-V5 binds to the C-terminal tag. Nine missense mutations in PMEL were discovered in individuals affected with PDS: one in the NTR, one in the CAF, six in the RPT and one in the Cyt. (B) Probing transfected HeLa cell lysates with anti-V5 shows that the Mβ band for the p.N111S sample has significantly lower relative intensity compared to WT (P < 0.05). (C) Probing transfected HeLa cell lysates with HMB45 did not detect p.N111S or p.A340V. MαC3 was not detected in p.G325V and had low intensity in p.S371T samples. A significantly lower amount of MαC1 was observed for p.E370D. Asterisks denote statistically significant changes, as quantified in Supplementary Material, Fig. S1B.
