Figure 1.
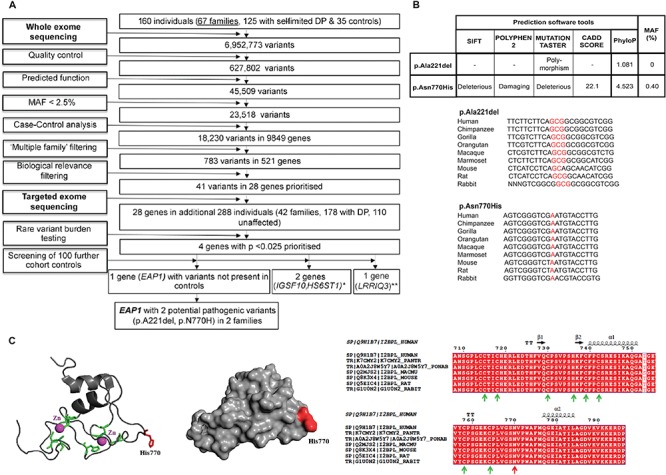
Filtering strategy to identify EAP1 as a candidate gene for self-limited DP, prediction of pathogenicity and conservation across species for EAP1 variants identified, and structural model of the Zn finger domain of EAP1. (A) WES was performed on DNA extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes of 160 individuals from our cohort (67 DP probands, 58 DP relatives and 35 controls). The exome sequences were aligned to the UCSC hg19 reference genome. Picard tools and the genome analysis toolkit were used to mark PCR duplicates, realign around indels, recalibrate quality scores and call variants. Variants were filtered for potential causal variants using filters for quality control, predicted functional annotation, MAF, case–control analysis, variants in multiple families and biological relevance. Targeted exome sequencing using a Fluidigm array of 28 candidate genes identified post-filtering was then performed in a further 42 families from the same cohort (288 individuals, 178 with DP and 110 controls). Variants post-targeted resequencing were filtered using the same criteria as the WES data. RVBT was performed with a multiple comparison adjustment applied post-hoc (17). Screening of 100 further cohort controls was via conventional Sanger sequencing. *Data published (15, 16). **Excluded due to the presence of variants in multiple controls. (B) Minor allele frequencies for ExAC Finnish population (accessed February 2018), conservation and pathogenicity scores (SIFT (37); Polyphen2 (36); MutationTaster (46)). Multiple sequence alignment (msa) was generated using MutationTaster (46). The p.Ala221 residue is highly conserved among different species, PhyloP score 1.801. The p.Asn770His is highly conserved among different species and the PhyloP score is 4.523. (C) The mutant 3D structure of the Zn finger domain of EAP1 is presented as a cartoon. The Zn atoms are presented as magenta spheres, the conserved C3HC4 residues (which bind Zn atoms) are presented in green and the mutant histidine (H) at position 770 is presented in red. The mutant His770, shown in red, is located on the surface of EAP1 and may be part of a protein–protein interaction site. The position of invariable residues C3HC4 is indicated with green arrows, whereas the position of N770 is indicated with a red arrow. The amino acid numbering and secondary structure is presented above the msa. C indicates cysteine.
