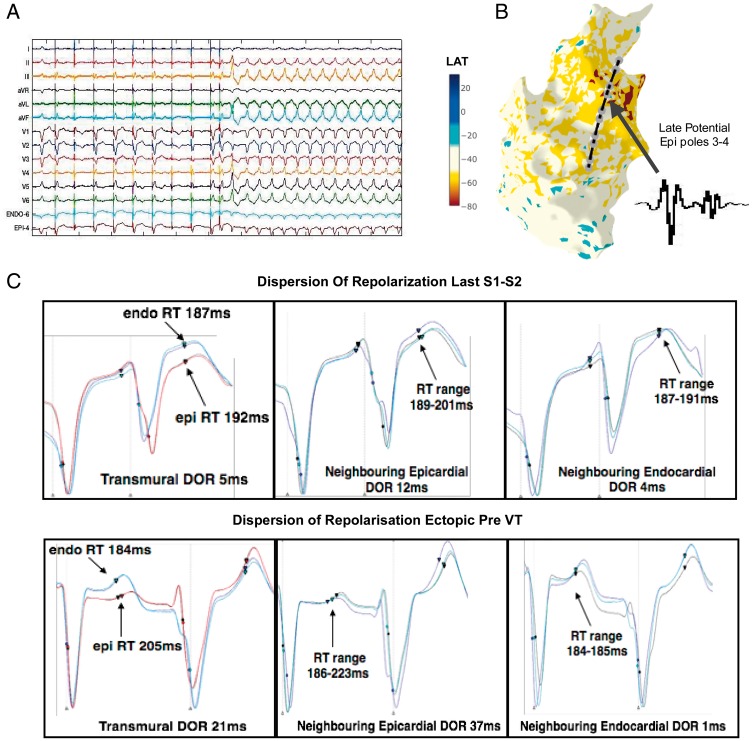
Figure 6.
DOR and initiation of VT in an example patient (Patient 6). (A) S1–S2 restitution protocol, showing 12-lead ECG and sample unipolar electrograms from the RV endocardium and RV epicardium. Following a train of S1 pacing, an S2 beat is delivered, following this an RV ectopic beat triggers sustained VT. (B) RV Endo geometry and activation mapping of the sustained VT showing earliest activation (red area), in the RVOT, along with location of transmurally opposed Endo and Epi decapolar catheters from the restitution study. Poles 3 and 4 of Epi catheter were located over a region of late potentials in sinus rhythm (inset). (C) DOR at Epi catheter pole location 3–4 (where fractionation was recorded), in the neighbouring Epi poles to 3–4, and in the neighbouring adjacent linear Endo poles. DOR is shown for the last S2 beat (above panel) and for the ectopic beat subsequent to this which initiates sustained VT. Circles represent activation time, triangles represent repolarization time. DOR, dispersion of repolarization; Endo, endocardial; Epi, epicardial; RV, right ventricular; RVOT, right ventricular outflow tract; VT, ventricular tachycardia.