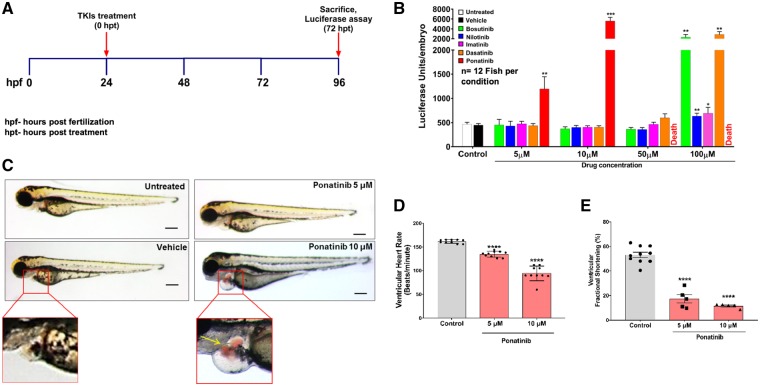
Figure 1.
Cardiotoxicity screening of approved CML TKIs in zebrafish. (A) Schematic of in vivo screening of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. (B) Luciferase-based reporter assay for rapid quantitative assessment of cardiac natriuretic peptide BNP expression in zebrafish embryos upon TKIs treatment. The nppb:F-Luc transgenic zebrafish embryos were treated with different concentration of TKIs. Ponatinib showed elevation in luciferase level when compared with control and other TKIs at 5 μM and 10 μM concentrations, while 50 μM and 100 μM ponatinib treatments leads to 100% lethality. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was conducted using two-way ANOVA post hoc Tukey test for comparison between DMSO vs. TKIs (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001); n=12 fish per condition. (C) Ponatinib cause pericardial oedema in zebrafish embryos. At 1 dpf, wild-type (AB) zebrafish embryos were treated with increasing concentrations of ponatinib and were assessed for phenotypic changes. After 72 h of treatment with ponatinib, zebrafish had extensive pericardial oedema at 5 μm and 10 μM when compared with vehicle-treated embryos. The red box displays the pericardial sac area. In ponatinib treated (10 µM) fish, ventricular contractions got perturbed, allowing blood to accumulate in both chambers, and pool just posterior to the atrium (yellow arrow). Scale bar-100 µm. (D) Ponatinib treatment reduces heart rate. Fish were treated for 72 h with ponatinib at 5 µM and 10 µM concentrations and ventricular contraction rate was determined (b.p.m.). Ponatinib treatment led to significant decline in the heart rate when compared with control. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA post hoc Tukey test for comparison between DMSO (control) vs. ponatinib (****P < 0.0001); n = 8–10 fish per condition. (E) Ponatinib treatment reduces fractional shortening. Ventricular function was assessed on zebrafish embryos exposed from 1 dpf to 4 dpf with vehicle or 5 μM, 10 μM concentrations of ponatinib. Ventricular end-diastolic dimension (EDD) and end-systolic dimension (ESD) in both long and short axes were quantified. Fractional shortening (FS) was then calculated as a measure of contractile function; n = 5–10 fish per condition. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA post hoc Tukey test for comparison between DMSO (control) vs. ponatinib (****P < 0.0001).