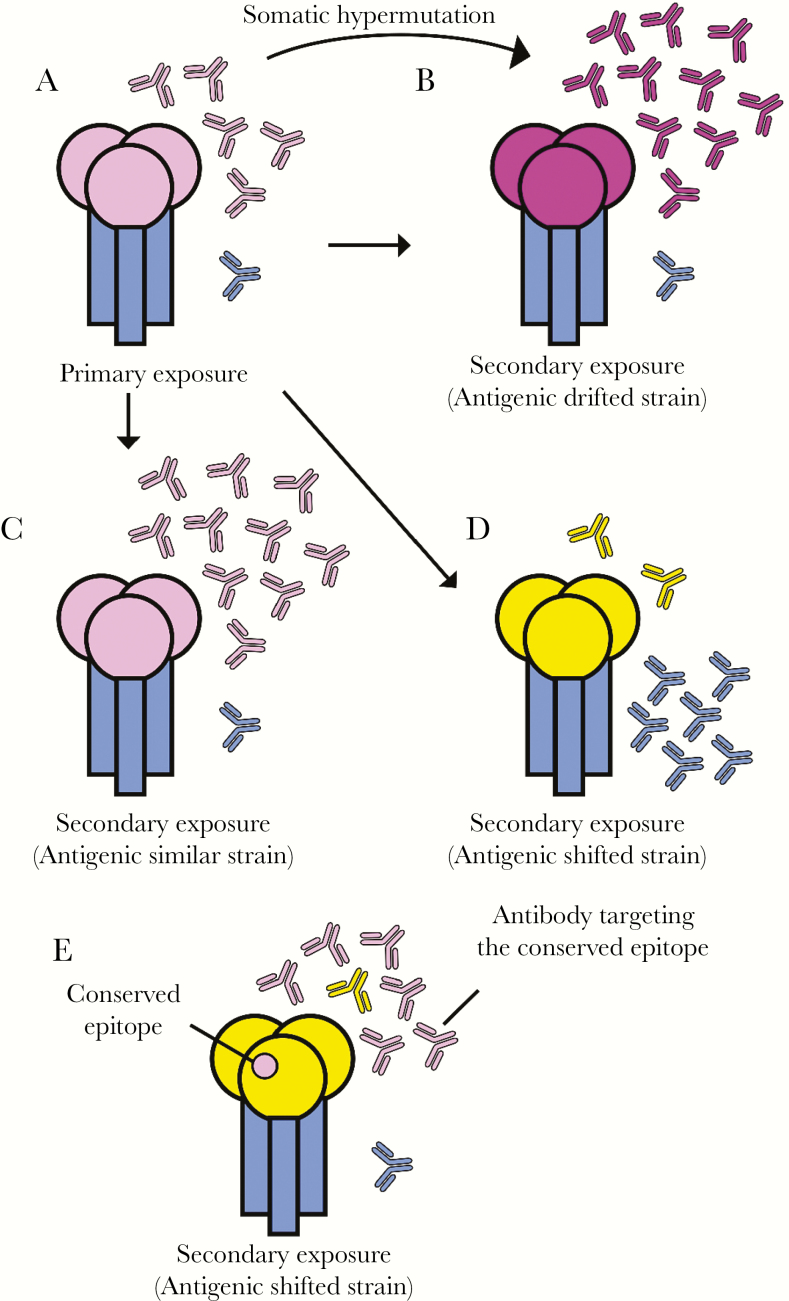
Figure 1.
Immunodominance of primary responses and recall responses against influenza hemagglutinin (HA). (A) The HA head domain (pink) is immunodominant in primary responses, whereas antibodies against the stem domain (blue) are rare. (B–C) Antibodies against the HA head remain dominant after exposure to antigenically similar (B) and antigenically drifted (C) seasonal viral strains. Antibodies elicited by antigenically drifted seasonal influenza virus strains often have high levels of somatic hypermutations that allow recognition of altered epitopes. (D–E) Antibodies against new pandemic viral strains tend to be more dominant initially against the (D) conserved HA stem, and (E) rare conserved epitopes, if any, in the HA head. Memory B cells producing antibodies against these conserved epitopes are preferentially boosted upon exposure to new pandemic viral strains. The color similarity of the HA head domain represents the similarity of the antigenicity in all figure panels.