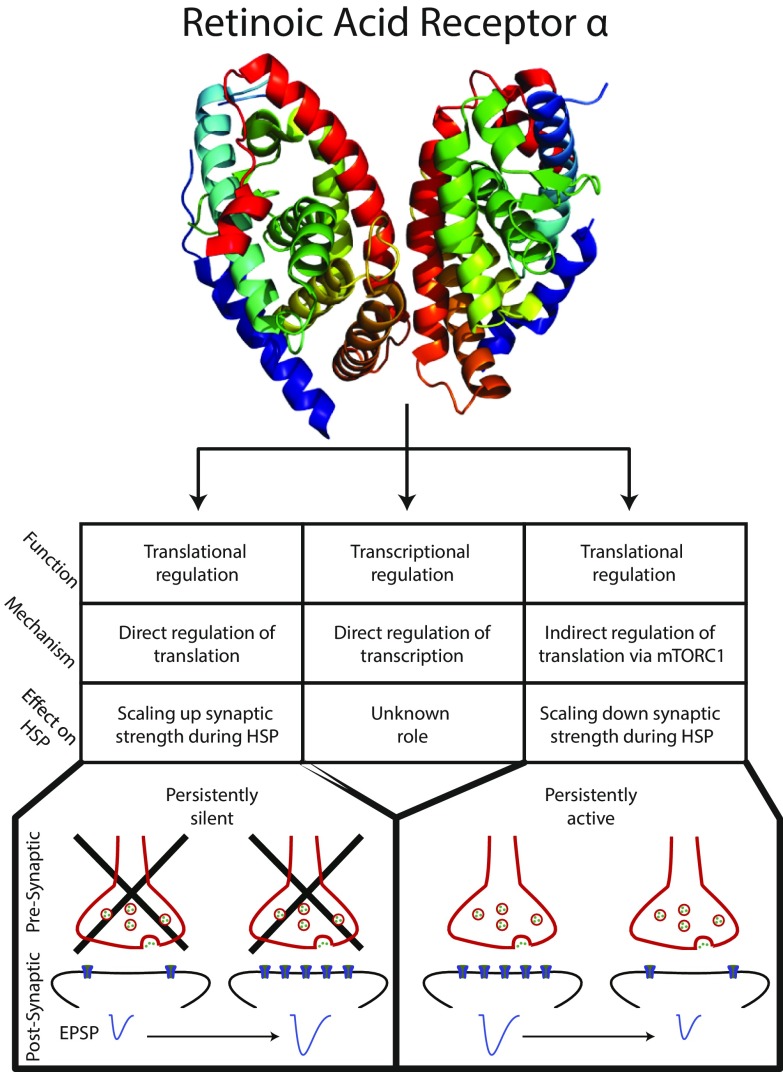
Fig. 1.
The many roles of RARα. (Top) Representation of RARα from ref. 3. (Middle) Three described functions of RARα: direct translational regulation (Left), direct transcriptional regulation (Center), and indirect translational regulation (Right). The transcriptional function of RARα has no known role in homeostatic synaptic plasticity (see Effect on HSP); however, both translational functions of RARα play important roles in HSP. The direct translational role of RARα (Bottom, Left) promotes the translation of AMPA receptors, which are inserted into the postsynaptic membrane after prolonged synaptic silencing, scaling up the synaptic response [illustrated by an increase in the evoked postsynaptic potential (EPSP)]. This is in direct opposition to the indirect translational role of RARα (Bottom, Right), which reduces translation of AMPA receptors by affecting the ERK-mTORC1 pathway, scaling down the synaptic response after persistent activity.