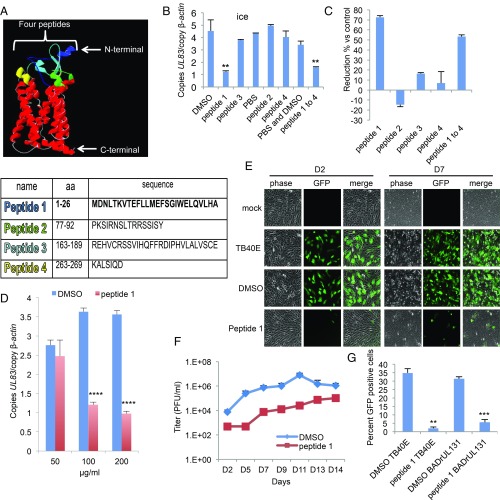
Fig. 4.
OR14I1 peptide inhibits HCMV binding and infection of epithelial cells. (A) OR14I1 model depicting four extracellular domains (blue, green, aqua, yellow) with their amino acid (aa) sequences listed below. (B) Binding assay. TB40E-GFP virus was preincubated with the indicated OR14I1 peptides (100 μg/mL) or relevant solvent followed by incubation of the virus with ARPE-19 cells on ice (MOI 2.0). After washing, cell surface-bound viral DNA (UL83) was quantified using qPCR and normalized to cellular DNA (β-actin). (C) The results in B are presented as the relative reduction in cell-bound viral DNA by peptide treatment relative to the relevant control. (D) Cell binding assay using the indicated concentrations of peptide 1 (MOI 2.0). (E) TB40E-GFP virus was preincubated with peptide 1 (100 μg/mL) or DMSO, followed by infection of ARPE-19 cells (MOI 2.0). Cells were imaged (10×) for GFP expression at 2 dpi (D2) and 7 dpi (D7). (F) Culture media supernatants from E were harvested on the indicated dpi and assayed for infectious virus by plaque assay. (G) TB40E-GFP or BADrUL131-GFP virus, both expressing the PC, was preincubated with peptide 1 (100 μg/mL) or DMSO before infection of ARPE-19 cells (MOI 2.0). Cells were fixed and assessed for GFP (green)-positive cells at 2 dpi. Data represent the mean of n = 3 experiments ±SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.