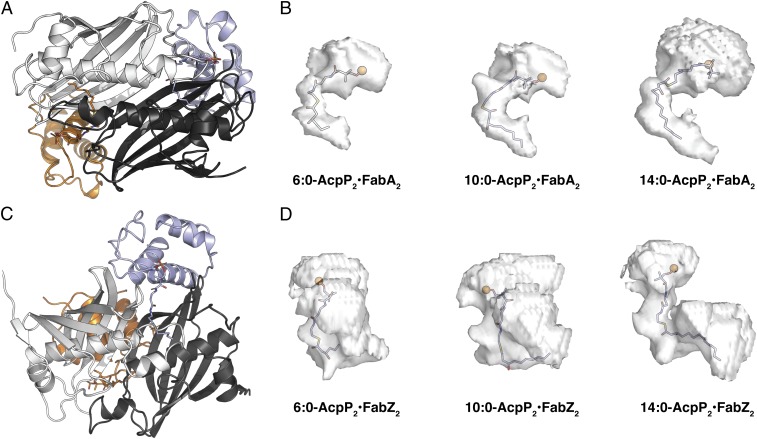
Fig. 8.
Cavities of the acyl-AcpP•FabA complexes sampled computationally. (A) Cartoon representation of the AcpP=FabA dimer oriented in a suitable manner (Bottom image) for the visualization of the acyl substrate chain within the FabA active site. (B) Isosurfaces of the acyl-AcpP•FabA complexes sampled via MD simulation. Ninety percent simulation data of each of these complexes possess an active site cavity that assumes a volume residing within the rendered isosurface. The phosphantethiene prosthetic group and acyl substrate are shown as sticks with the phosphantiethiene P as an orange sphere. Note that the computed cavities include unoccupied space (Upper regions of isosurfaces) between the carrier protein and the dehydratase (i.e., AcpP•DH interface). (C) Cartoon representation of the AcpP=FabZ dimer oriented in a suitable manner (Bottom image) for the visualization of the acyl substrate chain within the FabZ active site. (D) Isosurfaces of the acyl-AcpP•FabZ complexes sampled via MD simulation, rendered as in B.