Figure 1. Model proteins and design of experimental system.
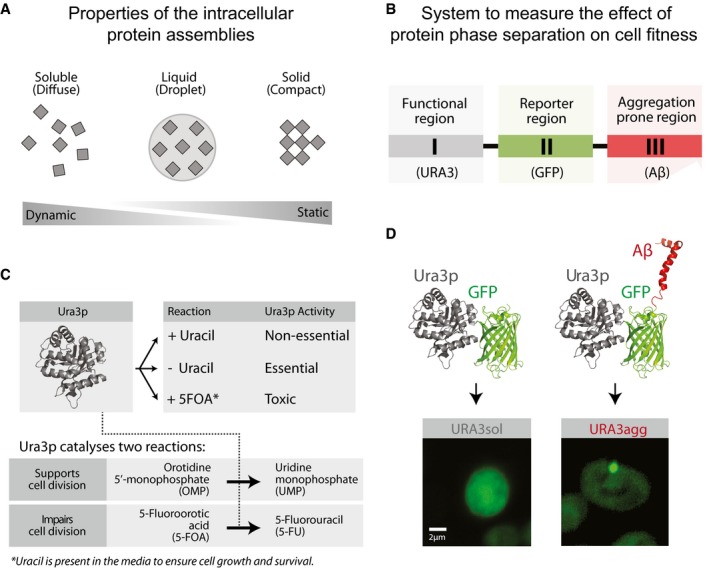
- Protein phase separation can lead to the formation of protein assemblies with varying dynamics. Soluble proteins may phase‐separate into liquid‐like droplets or insoluble deposits that, according to their viscoelastic properties and their ability to exchange components with the cytoplasm, vary from being dynamic to static.
- Design of the modular system to measure the effect of protein phase separation on cell fitness.
- Growth media composition and the essential/non‐essential/toxic roles of Ura3p.
- The model proteins consist of a fusion between Ura3p and GFP (URA3sol, left) and the amyloid‐β‐peptide of 42 residues (Aβ) (URA3agg, right). After 18 h of expression, Ura3psol remains homogeneously distributed whereas Ura3pagg is accumulated into intracellular foci.
