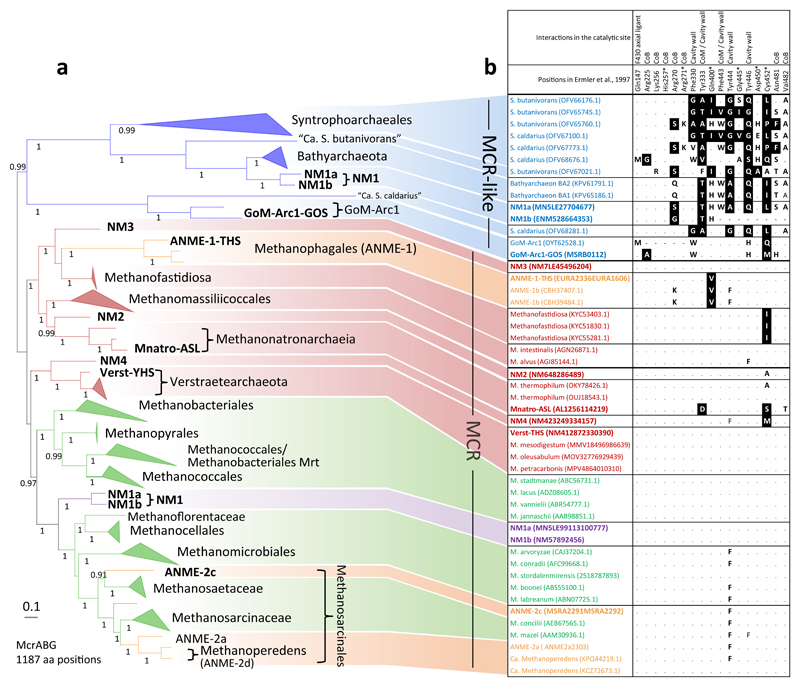
Figure 2.
Phylogeny of the MCR/MCR-like complex and conservation of important positions in the catalytic site. A) Unrooted Bayesian phylogeny (CAT+GTR+Γ4) based on a concatenation of McrABG/McrABG-like subunits (1,187 amino acid positions) from 109 genomes/MAGs (see Supplementary Table 6 for details). Node supports refer to posterior probabilities, and for reasons of readability only values above 0.8 are shown. The scale bar represents the average number of substitutions per site. The color code is similar to that in Fig. 1 with the exception of NM1 which have both an MCR-like (in blue) and a canonical MCR (in purple) (see text for discussion). B) Conservation of 17 residues previously described to interact with CoM, CoB, F430 cofactors, making part of the substrate cavity wall, or having post-translational modifications27,47,75. Replacement of conserved amino acids associated to a negative value in the Blosum45 matrix are indicated by white on black background, those with a null or positive value in the Blosum45 matrix are in bold, “.” indicate conserved positions and “-“ indicate missing positions in the sequence due to sequencing incompleteness.