Figure 5. Skin Tumors Induced by Chronic Exposure to UVB irradiation in Polθ−/−, Polη−/−, and Polη−/− Polθ−/− Mice.
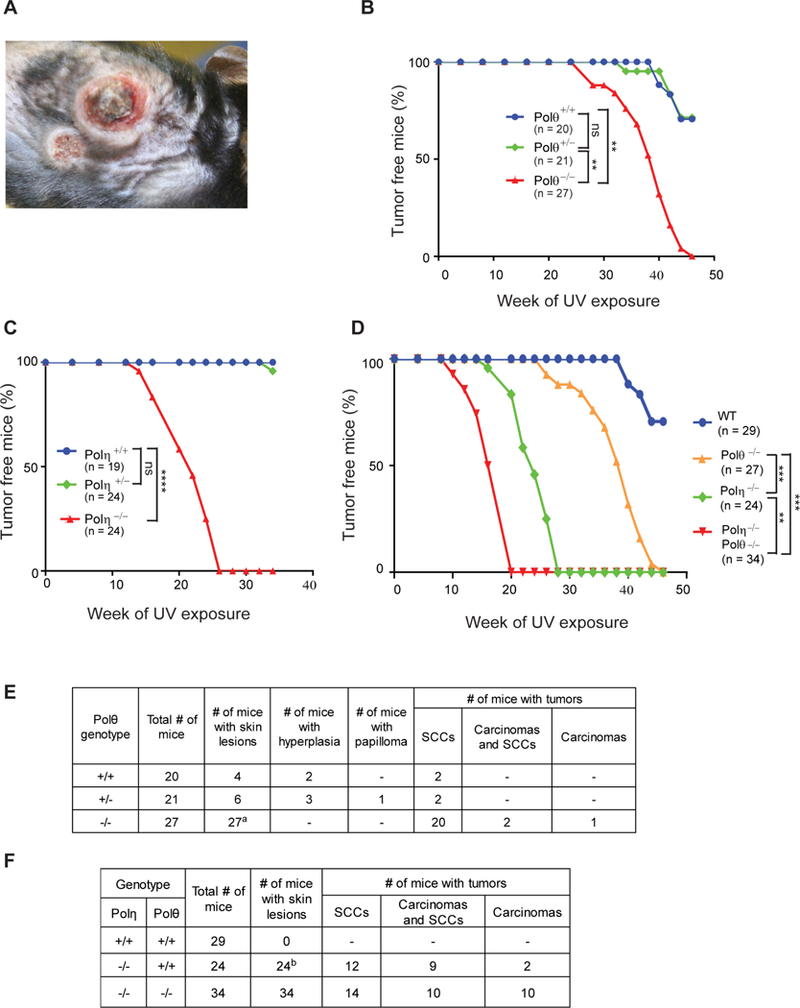
(A) UVB-induced skin tumors on the dorsal area of Polθ−/− mice at 42 weeks of UV exposure.
(B), (C), and (D) Kaplan-Meier curves of mice free of skin tumors after chronic UVB irradiation (2 KJ/m2, 3 times per week). (B) Polθ+/+, Polθ+/− and Polθ−/− mice. (C) Polη+/+, Polη+/− and Polη−/− mice. (D) WT, Polθ−/−, Polη−/− and Polη−/− Polθ−/− mice. Two way ANOVA p values, ns, non-significant; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001.
(E) Results of histopathological analyses of skin tumors from Polθ+/+, Polθ+/− and Polθ−/− mice. aTumors from 23 Polθ−/− mice were analyzed.
(F) Results of histopathological analyses of skin tumors from WT, Polη−/− and Polη−/− Polθ−/− mice. bTumors from 23 Polη−/− mice were analyzed.
See also Figures S5 and S6 and Table S4.
