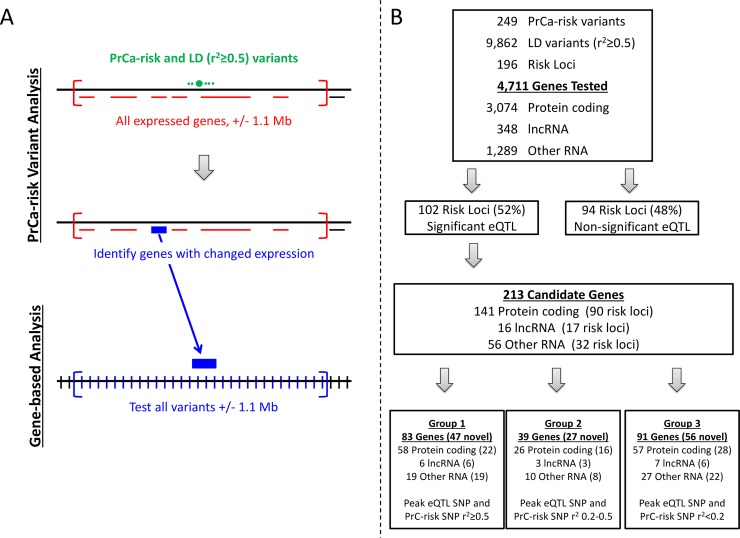
Fig 1. Study Design.
(A) Flow diagram of stages of analyses. In the variant-based analysis, PrCa-risk variant(s) (green bar) and all nearby variants in LD were tested for eQTL signals against all genes +/- 1.1 Mb (red lines) to identify target genes (blue line). In the gene-based analysis, all variants (blue bars) +/- 1.1 Mb from an identified gene (blue line) were evaluated for eQTL associations. (B) Numbers of variants and genes identified during analyses. A total of 10,111 variants (249 PrCa-risk and 9,613 LD variants) in 196 risk loci were tested in the first stage of analysis. Significant eQTL signals were found in 213 genes in 102 loci. Significant genes were identified as protein coding, lncRNA, or other RNA and then grouped according to the LD between the peak eQTL variant and the PrCa-risk variant. Numbers in the Groups indicate the total number of unique genes identified (number of unique novel genes identified. i.e., not previously reported in Thibodeau et al. 2016). Several genes fell into multiple groups due to the gene’s proximity to multiple risk loci. In this figure, each gene is counted only once and is included in the group with the highest LD with the PrCa-risk SNP. For a full list of all genes, please see S2 Table.