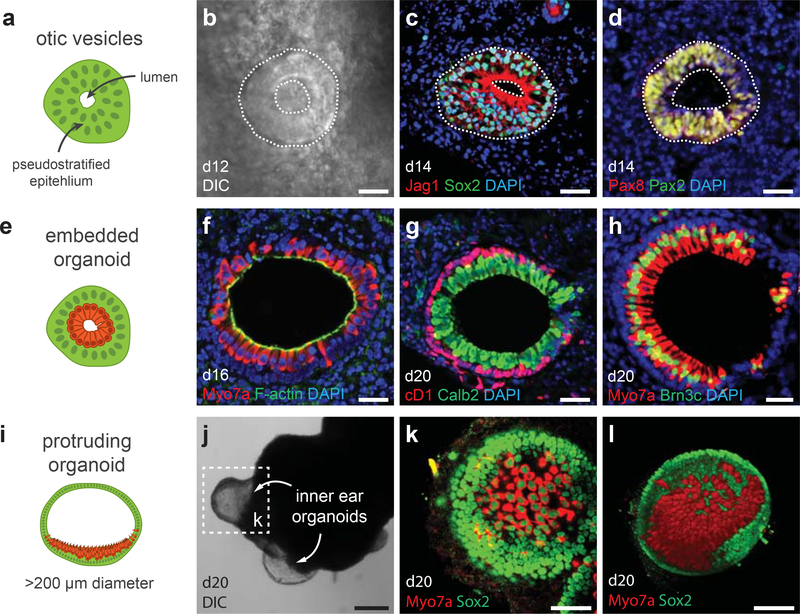
Figure 6: Hair cell induction and organoid types.
a, b, Otic vesicles can be seen using a conventional light microscope while aggregates are in culture. c, d, Otic vesicles express Jag1, Sox2, Pax2, and Pax8. e-l, There are two organoid variants: embedded (e-h) and protruding (i-l). The sensory epithelia of each inner ear organoids contain CyclinD1 (cD1)+ Sox2+ supporting cells and Myo7a+ Brn3c+ and Calretinin (Calb2)+ hair cells. i, j, Protruding organoids are typically >200 μm in diameter and are visible at low magnification or, occasionally, by the naked eye. See Table 1 for a list of antibodies used for characterization. Panels g and h were previously published in Supplementary Figure 13 of Koehler et al. Nature 2013. Scale bars, 250 (j), 100 (l), 50 (k), 25 (b-d) μm.