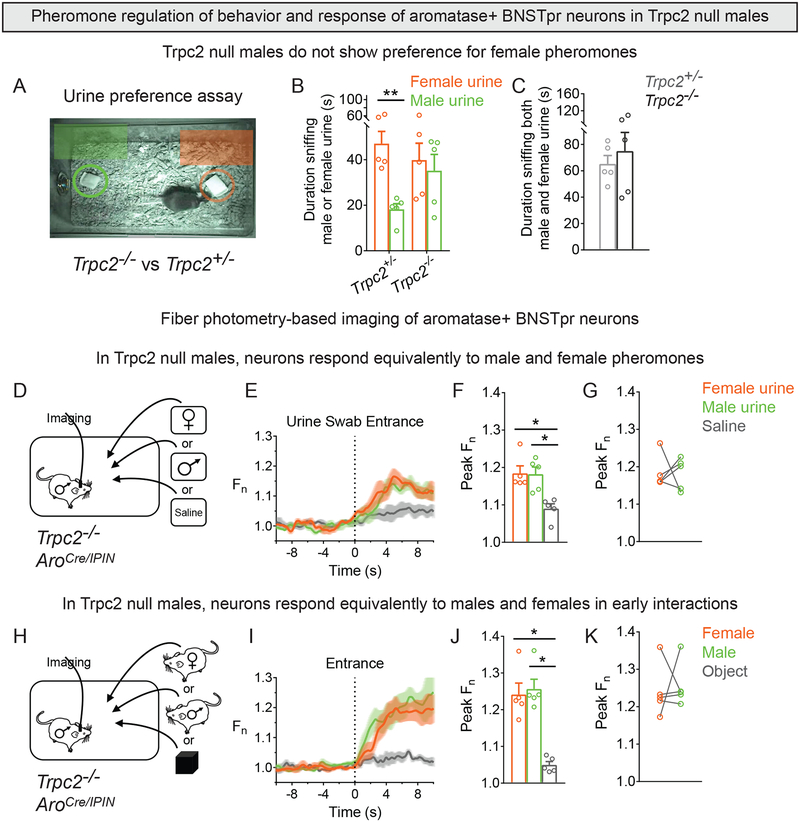
Figure 4: Sex-typical response of male AB neurons is dependent on pheromone sensing.
(A-C) Sexually naïve Trpc2−/− and Trpc2+/− males were tested for urine preference.
(B) Trpc2−/− males sniff male and female urine equally.
(C) Trpc2−/− and Trpc2+/− males sniff male and female urine for similar total duration.
(D-K) Fiber photometry of AB neurons in singly housed males exposed to urine swab (D-G) or male, female, or novel object inserted into the cage for 3 min (H-K).
(D) A cotton swab wetted with female or male urine or saline was inserted into the cage.
(E,F) Response of AB neurons was similar to male or female urine and larger than that to saline.
(G) Similar response to male or female urine.
(H) A WT male, receptive female, or novel object was inserted into the cage.
(I,J) Response of AB neurons was similar to male or female intruder and larger than that to the object.
(K) Similar response to male or female intruder.
Mean ± SEM. n = 5 males/genotype. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. See also Figure S4 and Movie S4.