Fig. 3.
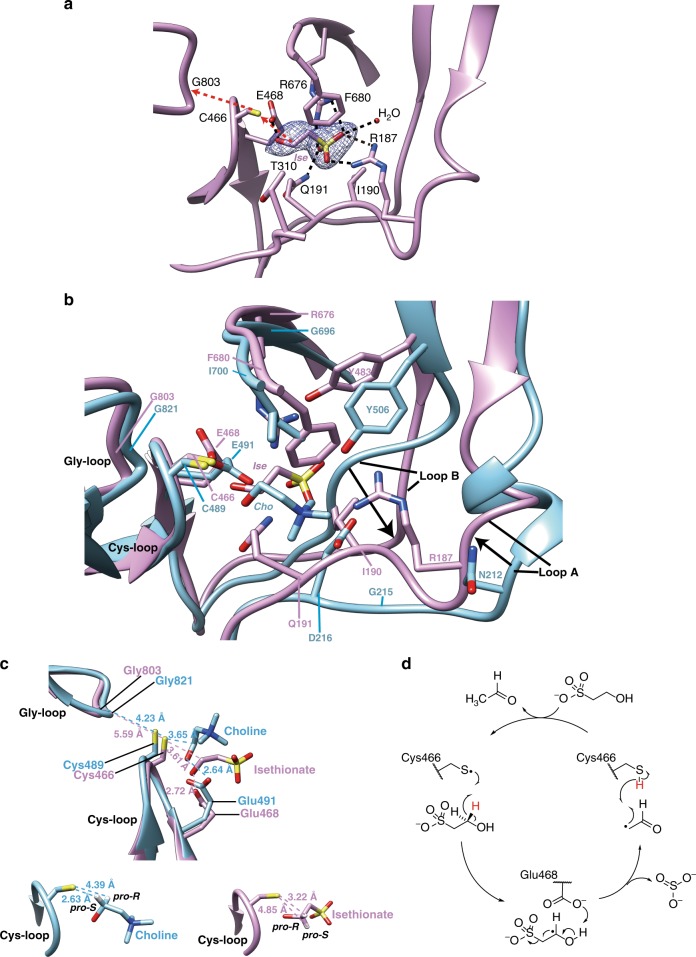
IseG active site structure. a IseG active site in complex with the substrate isethionate. The proposed pathway for hydrogen atom transfer is indicated by red arrows, and all hydrogen bonds are indicated by black dashed lines. 2Fo-Fc electron densities for isethionate are shown at 1.0σ. b Superposition of the IseG active site (plum) with CutC active site (cyan, PDB code 5FAU). Key residues involved in substrate binding and radical chemistry are displayed and labeled. The conformational changes in two substrate-coordinating loops are indicated by black arrows. c Structural model of the Gly-loop, Cys-loop, and the substrates. The distances between the key atoms are indicated. Comparison of the orientation of the modeled C1 hydrogens of isethionate (plum) and choline (cyan), suggesting that different enantiotopic hydrogens are abstracted by the thiyl radical. The distances between thiyl radical site and C1 hydrogens are labeled. d Proposed mechanism of isethionate cleavage by GUF (IseG). The thiyl radical, which is transiently generated by the G• cofactor in all GREs, abstracts a hydrogen (shown in red) from the substrate isethionate, and returns it to form the product acetaldehyde