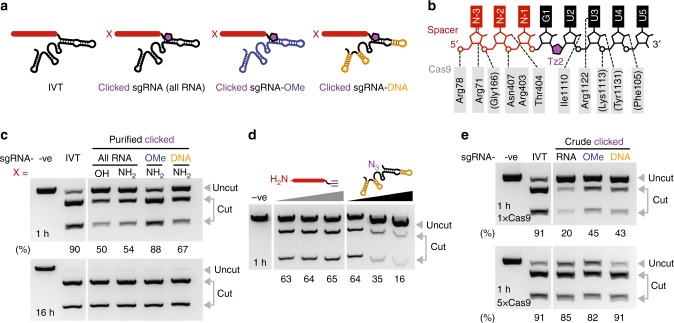
Fig. 2.
Clicked sgRNA constructs and their in vitro DNA cleavage activity. a illustrates the constructs tested (full sequences targeting plasmid pBR322 site 1 are in Supplementary Data 1). Note that when X = NH2, the modification is a 5′-C6-NH2 linker, and that when X = OH, there is no 5′ modification, only a 5′-OH group. b details the intermolecular interactions between Cas9 and the sgRNA based on PDB: 4OO8 (ref. 37), as well as the position of the triazole linkage. Note that the spacer is red, the Cas9-binding RNA is black and the Tz2 linkage is purple. c shows the activity of these constructs in Cas9-mediated DNA cleavage relative to in vitro transcribed (IVT) sgRNA at 1 and 16 h time points using 1× Cas9. d shows the inhibitory effects of the 79-mer but not the ~20-mer on Cas9 activity (0, 2 and 4 equivalents relative to clicked sgRNA-DNA, sequences can be found in Supplementary Data 2). e demonstrates that desalting CuAAC clicked constructs, without additional PAGE purification, still enables DNA cleavage, and that increasing Cas9 concentration five-fold (from 30 to 150 nM) allows comparable cleavage to IVT sgRNA. Note that for these clicked constructs X = 5′-C6-NH2. Cleavage values (under the gels) for c and e were quantified using an Agilent Bioanalyzer (Supplementary Fig. 4) where cleavage (%) = fcut/ftotal × 100 and f stands for fraction. Cleavage values (under the gel) for d was quantified using the same equation and ImageJ. Source Data are provided as a Source Data file