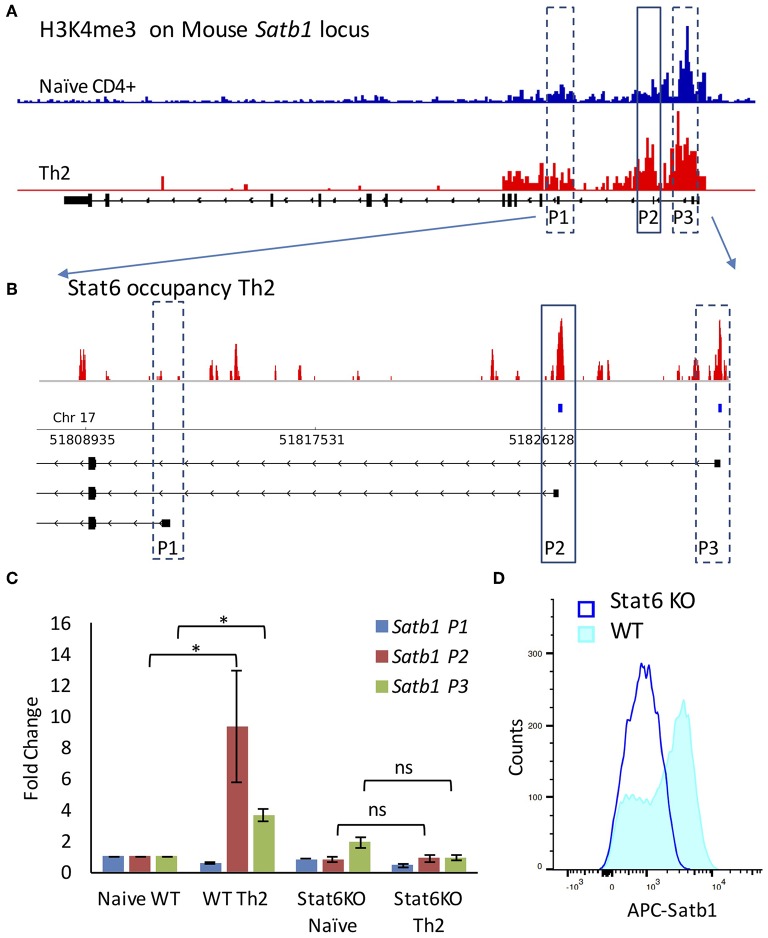
Figure 2.
Stat6 regulates P2 promoter usage in vivo. (A) ChIP-Seq analysis of H3K4me3 levels on Satb1 locus in naive CD4+ and Th2 cells (mouse mm10 genome assembly) performed as mentioned in “Materials and methods”. H3K4me3 marks are enriched at the P2 and P3 promoter regions in Th2 cells as compared to naive CD4+ T-cells. (B) ChIP-Seq analysis of Stat6 occupancy at the Satb1 alternative promoters in Th2 cells (enlarged view of Satb1 regulatory region). Stat6 ChIP-Seq aligned reads (first track) and significant peaks (second track) along with Satb1 alternative promoters in mouse (mm10 genome assembly). Stat6 binds to the Satb1 P2 promoter in T-helper cells. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of Satb1 alternative promoter usage (P1, P2, and P3) in naive CD4+ and Th2 cells performed in WT and Stat6 KO mice, respectively. Error bars represent SEM (N = 4); P-values were calculated using one-way ANOVA (* < 0.05). Stat6 KO adversely affects Satb1 alternative promoter usage. Unlike the wild type animals, no significant increase is observed in Satb1 P2 and P3 promoter usage in cells from Stat6 KO animals subjected to Th2 differentiation conditions. (D) Flow cytometry analysis for Satb1 protein expression in wild-type and Stat6 KO, respectively under Th2 differentiating conditions. Satb1 protein expression is not enhanced when naive T-cells from Stat6 KO animals are subjected to Th2 differentiation conditions.