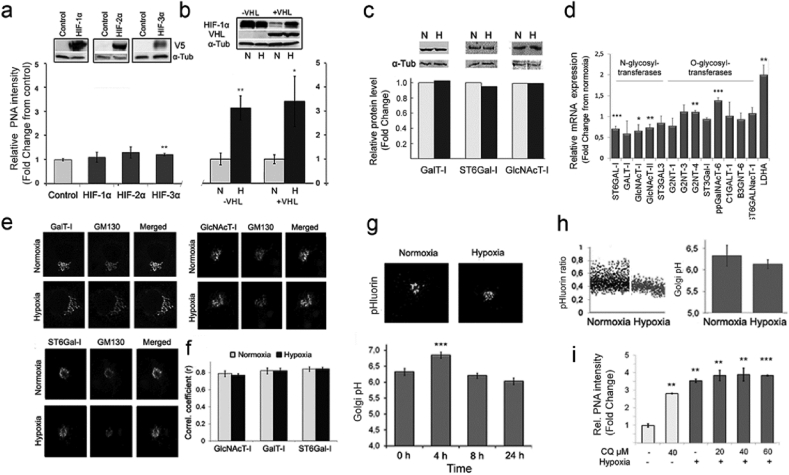
Fig. 2.
The effect of Hypoxia/HIFs on PNA staining and Golgi redox state changes in normoxic (N) and hypoxic (H) cells. a) PNA binding to normoxic COS-7 cells overexpressing HIFs (-1α, -2α, -3α). Cells expressing the depicted V5-taged HIF isoforms were stained with Alexa 594-conjugated PNA lectin before quantification of the bound lectin in triplicate (mean/cell ± SD, 90,000 cells/assay) with the high content imaging system. Insets show representative immunoblots for the HIF isoforms probed with V5-tag antibody. α-tubulin served as a loading control. b) PNA binding to VHL-deficient RCC4 and RCC4-reconstituted (RCC4pVHL) cells. Cells grown under normoxia and hypoxia were stained as above, and the PNA binding intensities were measured in triplicate as above. The changes are expressed as fold changes from normoxic control cells using the same scaling for comparison). The inset shows a representative Western blot probed with VHL protein-specific antibodies. (N, normoxia; H, hypoxia). Statistically significant changes are marked with stars (p < 0.05*, p < 0.01**, p < 0.001***). c-e) The effect of hypoxia on enzyme protein and mRNA levels, and their subcellular distribution as well as on Golgi pH homeostasis. c) Immunoblotting analyses of enzyme protein levels in COS-7 cells grown either in normoxia (N) or hypoxia (H). The samples were subjected to immunoprecipitation and then immunoblotting with the HA-tag specific antibodies. The band intensities were quantified to allow estimation of their relative amounts in normoxic and hypoxic cells. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. d) Quantitative RT- PCR analyses on the glycosyltransferases mRNA expression levels in the cells. mRNA levels were determined as described in “Materials and Methods” section. The values are expressed as fold changes from normoxic samples. Statistically significant changes are marked by stars (p < 0.05*, p < 0.01**, p < 0.001***). e) Subcellular distribution of the depicted enzymes in normoxic and hypoxic cells. Cells were transfected with the indicated mVenus-enzyme constructs, cultivated and processed for confocal immunofluorescence microscopy 24 h post-transfection and Z-stack imaging. Representative figures are shown for each enzyme together with the Golgi marker protein GM130 (red, stained with the protein specific antibody and Alexa 594-conjugated secondary antibody). f) Z-stack images were taken from 10 different Golgi elements (30 images per one Golgi area) to allow calculation of the Pearson's correlation coefficients. The Zen software (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) with an add-in module was used for the calculations. Statistically significant changes over the control are marked in the figures with stars (p < 0.05*, p < 0.01**, p < 0.001***). g-i) Golgi luminal pH in normoxic and hypoxic cells. Golgi pH was determined in cells expressing the Golgi-localized ratiometric pHluorin with the high content imaging system. The ratios were transformed to pH values (mean ± SD, n = 3, 15,000 cells each) using the formula derived from a pre-determined calibration curve (for details, see the “Materials and Methods” section in the Supplementary Appendix). g) Localization of the pH-sensitive probe (pHluorin) in the Golgi apparatus and time-dependent changes in the mean Golgi resting pH in hypoxic cells. h) Golgi resting pH determined in single cells in cells grown either in normoxia and hypoxia. Each dot in the graph (left) denotes to a single cell, while the bars (right) represent their mean values (±SD, n = 3, 15,000 cells each). The measurements were carried out 24 h post-transfection. i) Combined effects of chloroquine and hypoxia on PNA lectin binding in normoxic and hypoxic cells. Cells treated with or without the compound (Chloroquine, CQ, 40–60 μM) were grown in normoxic (light bars) and hypoxic (dark bars) conditions for 24 h before fixation, staining with the Alexa-594 conjugated PNA lectin and quantification of the bound lectin with the Operetta high content imaging system. The bars denote to fold changes (mean PNA intensity ± SD, n = 3, 15,000 cells each) from control cells (no CQ, normoxia). Statistically significant changes over the control are marked in the figures with stars (p < 0.05*, p < 0.01**, p < 0.001***).