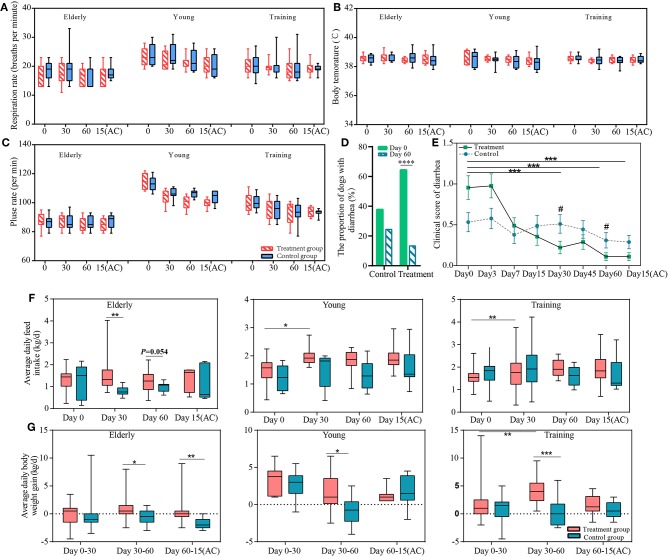
Figure 1.
The effects of the probiotics compound administration on host health. Respiration rate (A), body temperature (B), pulse rate (C) of three sample groups (elderly, young, and training groups); (D) the proportion of dogs with diarrhea at day 0 and day 60 of probiotic administration; (E) Changes in severity of diarrhea of the control and probiotic treatment groups. Error bars represent SEM. “***” represents comparison between different time points of the treatment group, ***P < 0.001; “#” represents comparison between the probiotic treatment and control groups at the same time point #P < 0.05. The changes in average daily (F) feed intake and (G) weight gain of the elderly, young, and training dogs, with or without probiotic treatment. Parameters were monitored at days 0, 30, 60, and 15(AC) (15 days after ceasing probiotic treatment). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.