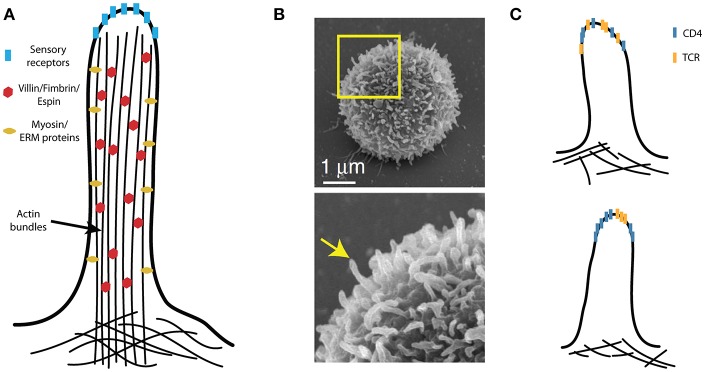
Figure 4.
Microvilli in T-cell activation. (A) A schematic illustration of a microvillus with villin, fimbrin and espin internally cross-linking compact actin bundles, which tightly fill the microvilli. The plasma membrane is also closely associated with the actin bundles via the ezrin, redoxin, and moesin (ERM) proteins; the dynamics of microvilli involve specialized myosins. The tips of the sensory (i.e., hairy) cell microvilli accumulate critical receptors. (B) The peripheral T cells are covered by finger-like protrusions that are reminiscent of microvilli on sensory cells. (C) Molecular organization of CD4 with respect to other T-cell signaling molecules (e.g., TCR) on microvilli remains unknown. These molecules may be randomly distributed (upper panel) or assembled into specific domains (lower panel). (B) Is adapted from Kim et al. (104) licensed under Creative Commons (CC BY 4.0).