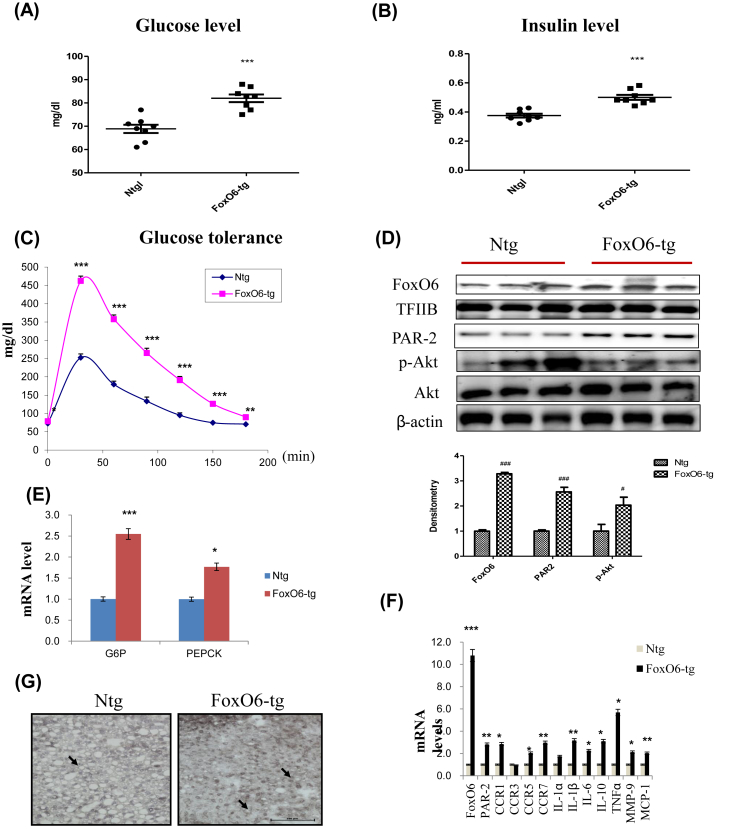
Fig. 1.
FoxO6 overexpression induced insulin resistance and cytokine production. Serum levels of pro-cytokines in mice injected with either FoxO6-CA or null adenoviral vectors, assessed over a period of 13 days (n = 6 in each group): (A) Glucose level (B) Insulin level (C) Glucose tolerance test in the serum of FoxO6-CA. (D) FoxO6, PAR2, p-Akt, and total-Akt levels were assessed using nuclear and cytosolic proteins in FoxO6-Tg mice. TFIIB is the loading control of the nuclear fraction. β-actin is the loading control of the cytosolic fractions. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Bars in densitometry data represent means ± SE, and significance was determined using an unpaired t-test: #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 vs. Ntg. (E) G6Pase and PEPCK mRNA levels of gluconeogenesis genes in FoxO6-tg liver. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 vs. Ntg. (F) The expression of relevant genes (FoxO6, PAR2, CCR1, CCR3, CCR5, CCR7, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, TNFα, MMP-9, and MCP-1) was analyzed by qPCR. The results were normalized with respect to actin levels. Real-time PCR analyses were performed to determine mRNA levels in liver tissues of FoxO6-Tg mice. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 vs. Ntg. (G) Macrophage infiltration was observed in the liver tissue of mice. F4/80 was used to identify macrophages, which can be seen as cells stained dark grey (marked with an arrow) in FoxO6-Tg and Ntg (×20).