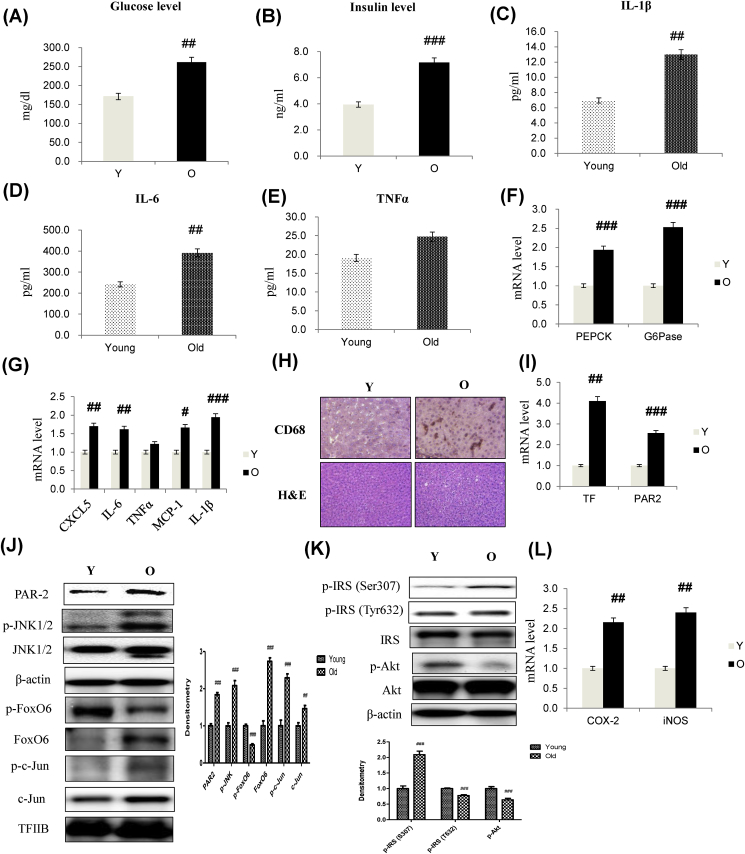
Fig. 7.
Aging-induced insulin resistance and expression of pro-inflammatory genes through TF/PAR2 signaling. To test the relationship among aging, insulin resistance, and the expression of pro-inflammatory genes, 6- and 24-month-old male Fischer 344 rats were used. (A) Glucose level (B) Insulin level in serum of aged models. Cytokine levels of (C) IL-1β (D) IL-6 (E) TNFα in serum using ELISA assay. The results shown are representative of three experiments. The data are expressed as a mean ± SEM (n = 6). ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. Young. (F) G6Pase and PEPCK mRNA (G) CXCL5, IL-6, TNFα, MCP-1, and IL-1β mRNA. Real-time PCR analyses were performed to determine mRNA levels in liver tissues of young (6 months) and old (24 months) rats. The results shown are representative of three experiments. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. Young. (H) Representative macrophage recruitment immunohistochemistry. Liver sections were stained with a specific antibody against the macrophage marker, CD68. (I) mRNA levels of TF and PAR2 genes. ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. Young. Western blot analyses of liver nuclear and cytosolic (J) PAR2, p-JNK1/2, JNK1/2, p-FoxO6, FoxO6, p-c-Jun, c-Jun (K) p-IRS1 (S307), p-IRS (T632), IRS, p-Akt, and total-Akt levels were performed using nuclear and cytosolic proteins from aged rats. Results are representative of three independent experiments. TFIIB was the loading control of the nuclear fraction. β-actin was the loading control of the cytosolic fractions. Bars in densitometry data represent means ± SE, and significance was determined using an unpaired t-test: ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. Young. (L) COX-2 and iNOS mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory genes. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. ##p < 0.01 vs. Young.