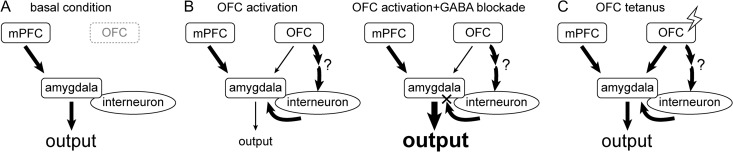
Figure 6.
One potential model that may account for the OFC modulation of the mPFC–amygdala pathway. Compared with (A) basal condition, (B) pharmacological or electrical activation of the OFC exerted an inhibitory modulation of the mPFC–amygdala pathway (left), which was reversed by intra-amygdala blockade of GABAergic receptors (right). (C) Tetanization of the OFC-related pathways results in a loss of OFC control over the mPFC–amygdala pathway, presumably because of a selective enhancement of the OFC–amygdala principle neuron input. Abbreviations refer to Figure 1.