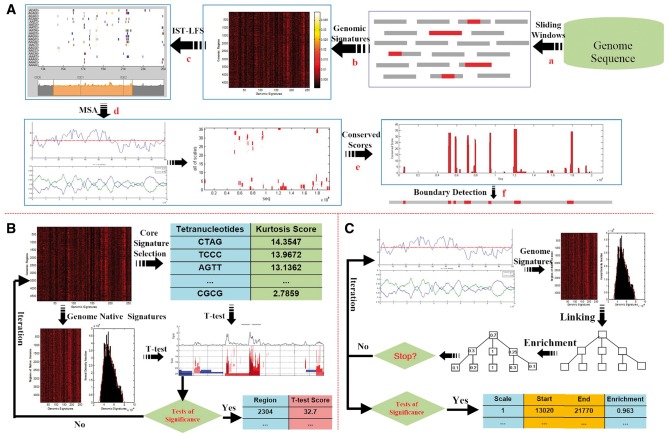
Figure 1.
Overview of the MTGIpick algorithm. (A) The workflow of the MTGIpick algorithm, with (a) split a genome into non-overlapping windows with a size of 1 kb; (b) extract genomic signatures represented as a heatmap; (c) score each window using IST-LFS; (d) identify large segments using MSA; (e) calculate conserved score of the predicted genomic islands; and (f) refine the boundaries of the GIs using the GC-MJSD method. (B) The workflow of the IST-LFS algorithm, in which signatures of the host are extracted using the CIWV, and core signatures are selected based on ordered kurtosis. During an iteration, we score each window using the two-sample t-test and select the windows whose scores are large enough to be considered to be statistically significant. (C) The workflow of the MSA algorithm. Starting from the IST-LFS scores and GC content, we select signatures of the host using the CIWV. During an iteration, we construct a continuous linear scale-space using a blurring strategy, score the enrichment of all the segments using the Z test and select the windows whose enrichment scores are large enough to be considered to be statistically significant.