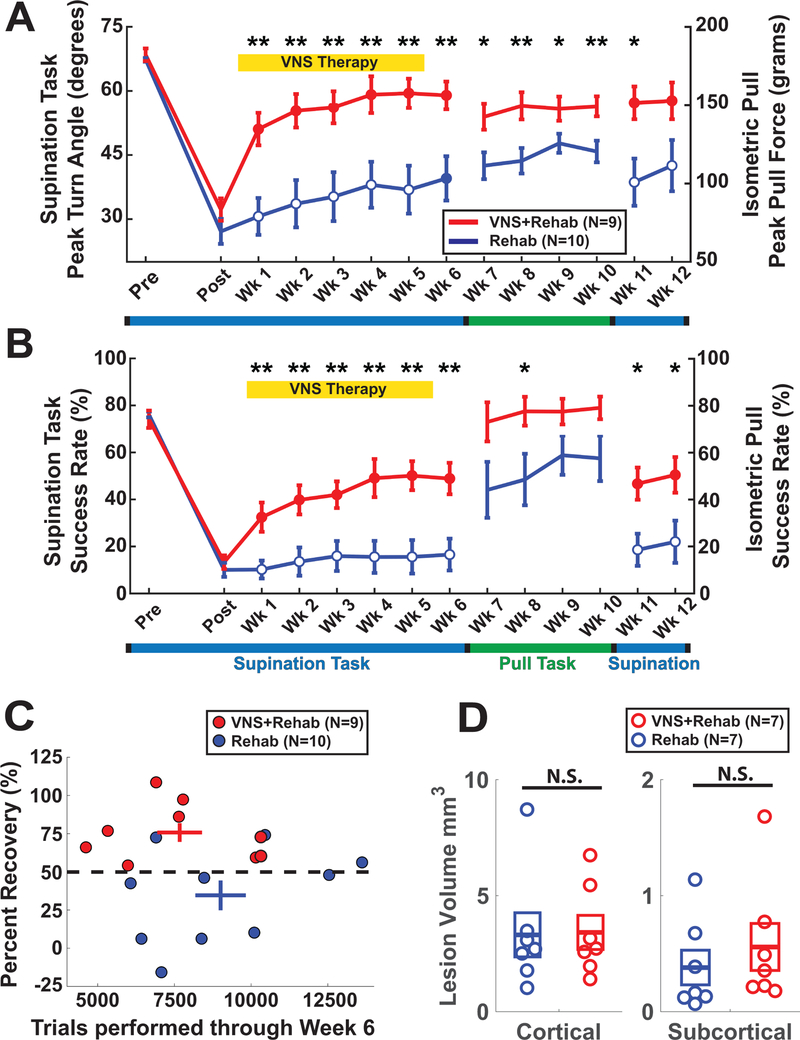
Figure 2.
VNS paired with rehabilitative training improves forelimb function after stroke. (A) VNS improves recovery of supination turn angle during task-oriented rehabilitative training (Post-Wk6). The beneficial effects of VNS delivered on the supination task transfer to the isometric pull task although no VNS is delivered during this time (Wk7-Wk10). Furthermore, when subjects are retested on the supination task, the benefits of VNS were maintained 7 weeks following the cessation of stimulation (Wk11 & 12). (B) Similar effects were observed for success rate. (C) All subjects (9 of 9) in the VNS+Rehab group achieved at least 50% recovery of function, compared to only 3 of 10 Rehab subjects. No differences in trials performed through Week 6 were observed across groups. (D) No significant difference in cortical or subcortical lesion volume was observed. Asterisks denote: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 between the VNS+Rehab and Rehab groups. Filled circles denote significant difference compared to Post timepoint.