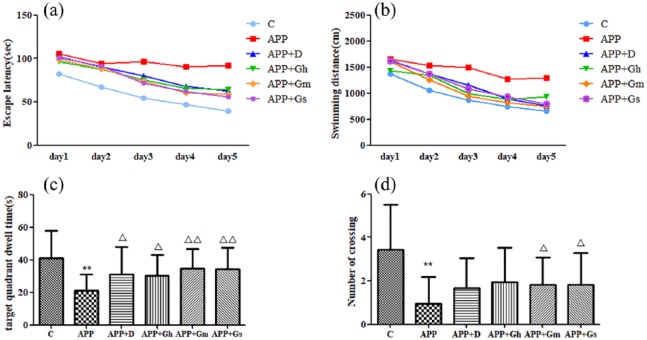
Figure 1.
Effect of GAPT on (a) escape latency, (b) swimming distances, (c) target quadrant dwelling time and (d) number of APP/PS1 transgenic mice crossing the platform in the MWM test. Control: C57BL/6J mice; APP: APP/PS1 mice; APP + D: donepezil; APP + Gs: GAPT small dose; APP + Gm: GAPT middle dose; APP + Gh: GAPT high dose.
**P < 0.01 versus control group, △P < 0.05 versus model group and △△P < 0.01 versus model group; ANOVA. Each group showed a decreasing trend with the increase in training times. The escape latency and swimming distances of the control group were significantly decreased from the first day compared to those of the model group (P < 0.01). On the fourth day and fifth day, the escape latencies of all intervention groups were shortened (P < 0.05). The target quadrant dwelling time of each intervention group was increased compared with the model group (P < 0.05). The GAPT middle and small dose groups crossed the target platform obviously more frequently than the model group (P < 0.05).