Fig. 4.
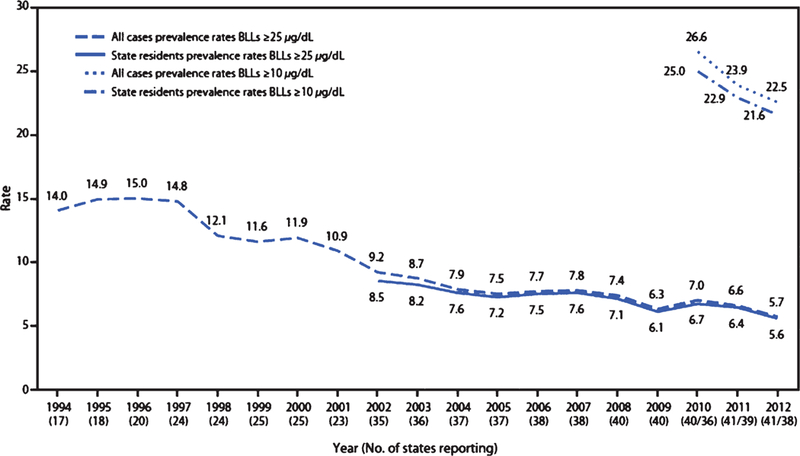
Adult blood-lead levels have continued to decline over the past two decades. This figure depicts the U.S. national prevalence rate (per 100,000 employed adults aged ≥16 years) of reported cases of elevated blood-lead levels (≥10 µg/dL and ≥25 µg/dL) by year from the State Adult Blood Epidemiology and Surveillance Programs, United States, 1994–2012. Reproduced from Alarcon et al. [151], US-Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
