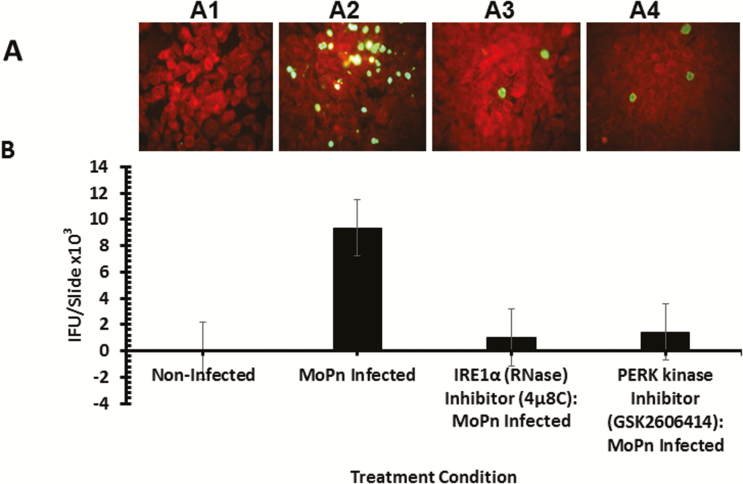
Figure 6.
Role of the IRE1α and PERK signaling pathways of UPR in Chlamydia replication in vitro. Fluorescence microscope images and bar chart of MoPn infectious-forming units recovered from C57epi cells treated with or without IRE1α RNase or PERK inhibitors. A, Fluorescence microscope images of noninfected C57epi cells (A1), C57epi cells infected with MoPn (A2), and C57epi cells infected with MoPn and treated with IRE1α RNase (A3) or PERK kinase (A4) inhibitor. B, Bar chart of MoPn infectious-forming units recovered per slide of noninfected, MoPn (MOI 5)–infected, and MoPn (MOI 5)–infected/treatment with IRE1α RNase or PERK kinase inhibitors. All cultures were incubated for 48 hours. Abbreviations: C57epi cells, mouse oviduct epithelial cells; IRE1α, inositol-requiring enzyme-1α; MOI, multiplicity of infection; MoPn, mouse pneumonitis; NI, noninfected; PERK, protein kinase RNA-activated–like ER kinase; RNase, ribonuclease; UPR, unfolded protein response.