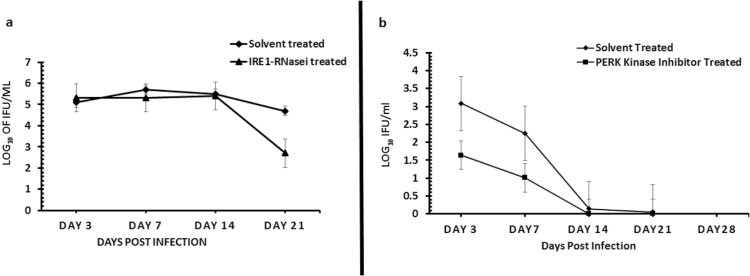
Figure 7.
Role of the IRE1α (7A) and PERK (7B) signaling pathways of UPR in Chlamydia replication in vivo. Graph shows the number of inclusion-forming units recovered from mice infected with C. muridarum (MoPn) and treated/untreated with inhibitor of IRE1α RNase after a primary infection (7A) or PERK kinase after a secondary infection (7B) activity. The triangle symbol plot represents mice infected intravaginally with MoPn and treated intravaginally with inhibitor of IRE1α RNase or PERK kinase activity. The diamond symbol plot represents mice infected intravaginally with MoPn and treated intravaginally with 2% DMSO (solvent concentration used in the preparation of IRE1α RNase or PERK kinase inhibitor). The y-axis represents the number of inclusion-forming units recovered; the x-axis is the number of days postinfection. Abbreviations: DMSO, dimethylsulphoxide; IRE1α, inositol-requiring enzyme-1α; MoPn, mouse pneumonitis; PERK, protein kinase RNA-activated–like ER kinase; RNase, ribonuclease; UPR, unfolded protein response.