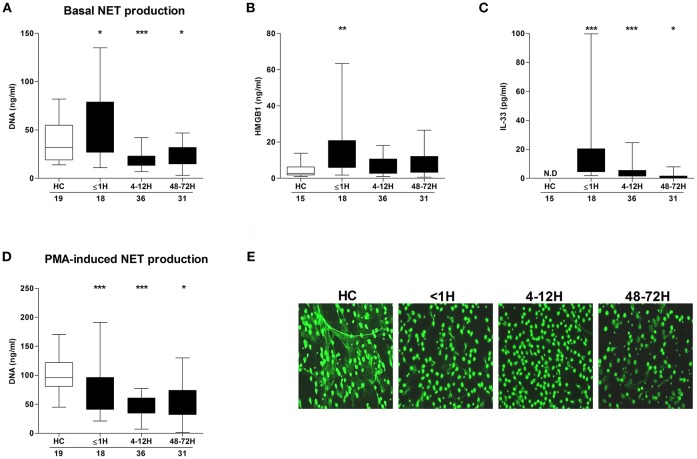
Figure 1.
Effect of traumatic injury on PMA-induced NET formation. (A) Basal NET generation by resting neutrophils isolated from healthy controls (HC) and trauma patients as assessed by DNA concentration in cell free supernatants following a 3 h in vitro culture. (B) HMGB-1 and (C) IL-33 concentrations in serum samples from HC and trauma patients. IL-33 levels were undetectable (N.D) in serum samples from HC. (D,E) Following a 3 h in vitro stimulation with PMA, NET production by neutrophils from HC and trauma patients was compared by measuring DNA concentration in cell free supernatants (D) and fluorescence microscopy (E). For supernatant analysis, number of samples are shown below each time-point. For microscope images, HC (n = 12), ≤1 h (n = 6), 4–12 h (n = 6), and 48–72 h (n = 8). *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001 vs. HC.