Figure 6.
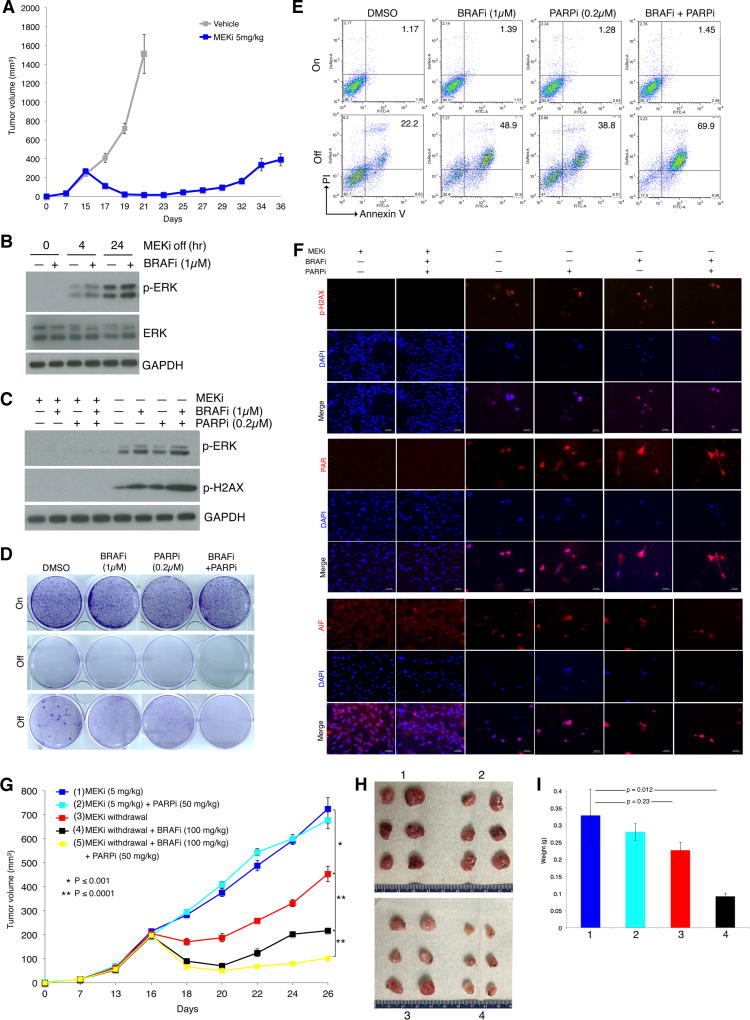
BRAF and PARP inhibitors augment MEKi addiction of MUTNras murine melanoma in an immune competent host. (A) Tumor volumes (mean ± SEM) of TpLN61R murine melanoma cells transplanted in C57BL/6 mice in response to daily gavage with the vehicle (n = 6) or trametinib (5 mg/kg; n = 6). One resistant tumor on day 36 was dissociated and cultured as a MEKi-resistant cell line (NILR2R). (B) Western blot levels of p-ERK, ERK, and the loading control GAPDH in the MEKi-resistant MUTNras SDR line, NILR2R, with indicated hrs off MEKi/trametinib (0.1 µM) treatment, with or without BRAFi/vemurafenib (1 µM) treatment. (C) Analysis of NILR2R protein lysates by Western blots of p-ERK and p-H2AX levels on or off MAPKi(s), with or without BRAFi (1µM) and/or PARPi (0.2µM) treatment for 3 d. (D–E) Clonogenic growth (D; 8 d) and percentages of Annexin V/PI-positive dead cells (E; 5 d) in NILR2R, on or off MEKi/trametinib (0.1 µM), with or without BRAFi/vemurafenib (1 µM) and/or PARPi (0.2µM) treatments. For D, cultures were seeded at 30K cells per well, except for the third row where cultures were seeded at 150K cells per well. (F) Levels and/or subcellular localization of p-H2AX, PAR, and AIF in NILR2R, on or off MEKi for 3 d, with or without BRAFi and/or PARPi treatment. Ruler, 20 µm. (G) Trametinib-resistant NILR2R cells were transplanted subcutaneously in C57BL/6 mice with daily trametinib (5 mg/kg) gavage until segregation into five groups (n=6 per group). Tumor volumes are shown as means ± SEM. P values, Student’s t-test. (H) Pictures of tumors from the first four experimental groups (mice sacrificed due to tumor ulceration) in G at day 26. (I) Tumor weights (means ± SEM; p value, unpaired two-way t-test) of the first four experimental groups in G.