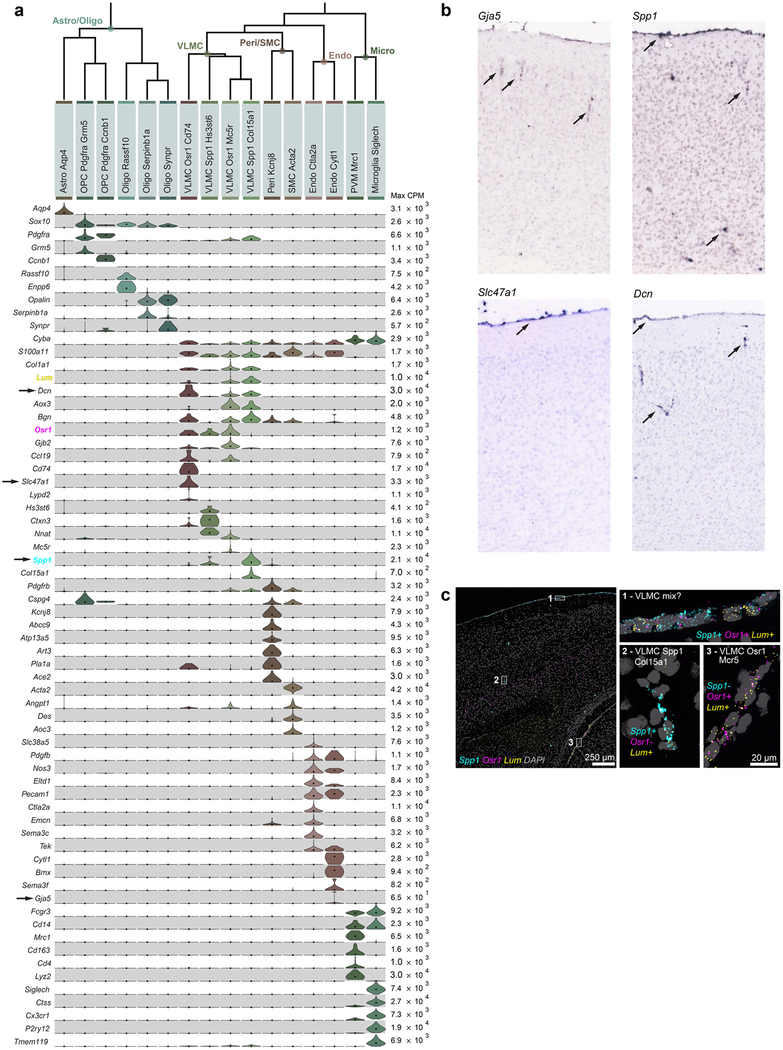
Extended Data Fig. 9 |. Non-neuronal cell types.
a, Non-neuronal cells (n = 1,383 cells) are divided into two major branches according to their developmental origin: neuroectoderm-derived branch, which contains astrocytes and oligodendrocytes (left), and non-neuroectoderm-derived, which includes immune cells (microglia, perivascular macrophages), blood vessel-associated cells (smooth muscle cells, pericytes and endothelial cells), and vascular leptomeningeal cells (VLMCs, right). All have been detected in both ALM and VISp, except VLMC-Osr1-Cd74, which may be rare (12 cells total) and may also be detected in ALM with further sampling. Violin plots represent distributions of individual marker gene expression in single cells within each cluster. Rows are genes, median values are black dots, and values within rows are normalized between 0 and the maximum expression value for each gene (right edge of each row) and displayed on a linear scale. We identify astrocytes based on expression of Aqp477. Oligodendrocyte lineage cells express Sox1078. Oligodendrocyte precursor cells are marked by expression of Pdgfra and absence of Col1a177,78, with dividing oligodendrocyte precursor cells expressing Ccnb1. Newly generated oligodendrocytes (Oligo-Rassf10) express Enpp6, whereas myelinating oligodendrocytes (Oligo-Serpinb1a/Synpr) express Opalin79. Two related types of immune cells coexpress Cd14 and Fcgr3, and can be identified as microglia by expression of Siglech80 and Tmem11981, and perivascular macrophages by expression of Mrc1, Lyve119 and Cd16381. We identify two related types of blood vessel- associated cells as pericytes and smooth muscle cells (SMCs) based on their expression of Cspg4 and Acta2 (reviewed previously82). We assign SMC identity to SMC-Acta2, which strongly expresses Acta2 (smooth muscle actin). We assign pericyte identity to the Peri-Kcnj8 cluster based on specific expression of pericyte markers Kcnj8 and Abcc983. We define additional markers uniquely expressed in this cell type (Atp13a5, Art3, Pla1a and Ace2) that may help solidify pericyte identity in future studies. We identify one type of endothelial cells (Endo-Slc38a5) based on expression of previously characterized endothelial markers, Tek, Pdgfb, Nos3, Eltd1 and Pecam1. We identify VLMC types based on their unique expression of Lum and Col1a178,84. We define four types based on differential gene expression. Markers examined in b and c are highlighted by arrows and colours, respectively. b, RNA ISH for some of non-neuronal markers from the Allen Brian Atlas25. Images contain regions of interest from representative sections selected from individual whole-brain RNA ISH experiments. Spp1 mRNA is detected in the meninges and scattered in the cortex, corresponding to VLMCs, as well as select Pvalb and Sst types. Gja5 mRNA labels vessel-like structures in the grey matter, probably corresponding to the Endo-Slc38a5 cluster. Slc47a1 is specific to the VLMC-Osr1-Cd74 type, which appears to be restricted to pia. Dcn is expressed in three VLMC types, and its expression is seen in the pia and vessel-like structures in the cortex. The number of whole-brain experiments per gene available in the Allen Brain Atlas is as follows: Spp1: n = 4 brains (2 sagittal, 2 coronal); Gja5: n = 2 brains (2 sagittal); Slc47a1: n = 1 brain (sagittal); Dcn: n = 3 brains (2 sagittal, 1 coronal). c, Single-molecule RNA FISH by RNAscope for Osr1, Spp1 and Lum mRNAs shows labelling at the pial surface and surrounding vessel-like structures. Images are representative of two independent RNAscope experiments on n = 2 brains. On the basis of the coexpression of marker genes shown in a, VLMCs within the grey matter (expanded region 2) are probably the VLMC-Spp1-Col15a1 type, whereas VLMCs in pia between cortex and tectum (expanded region 3) are probably VLMC-Osr1-Mc5r. The surface VLMCs (expanded region 1) appear to express all three markers, which are usually not co-detected in single cells by RNA-seq (a). This finding could be explained by a possibility that region 1 may contain two or more types of spatially appositioned VLMCs, for example, VLMC-Osr1-Cd74 (based on Slc47a1 expression shown in b), as well as one of the Lum+ types (VLMC-Osr1-Mc5r and/or VLMC-Spp1-Col15a1).Extended Data Fig. 10 | See next page for caption.