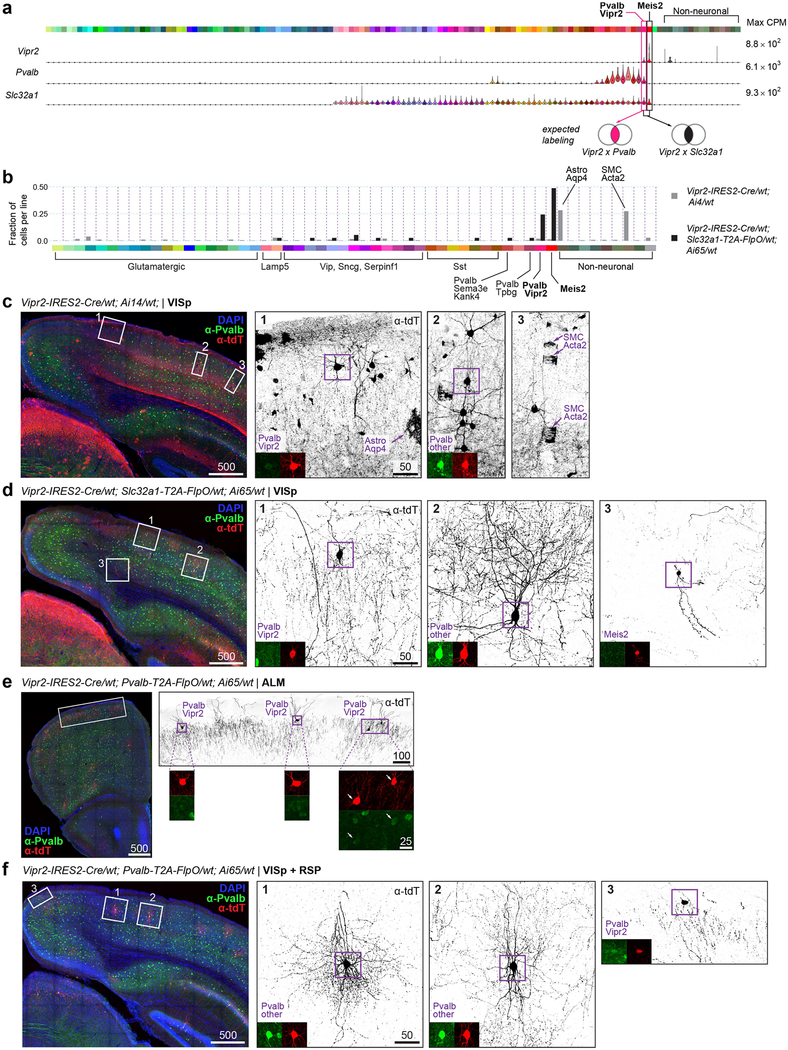
Extended Data Fig. 13 |. A new tool, Vipr2-IRES2-Cre, for access to select transcriptomically defined cell types.
a, Expression of select marker genes in our transcriptomically defined cell types (colour bar on top) represented as violin plots for all cluster-assigned cells (n = 23,822 cells; 133 clusters). Median values are black dots. Each row is scaled to the maximum expression value shown to the right of the plot (in CPM), and displayed on a linear scale. Venn diagrams represent expected cell type labelling by genetic tools described below. A new transgenic line, Vipr2-IRES2-cre, was created to label Pvalb-Vipr2 and Meis2 types. Unlike the previously developed Nkx2.1-creERT2 line87, this line does not require tamoxifen induction for chandelier cell labelling (corresponding to Pvalb-Vipr2). b-f, Specificity of this recombinase line was tested by scRNA-seq and immunohistochemistry. b, scRNA-seq and clustering with other cells revealed cell types labelled by two mouse genotypes on the right. Types are labelled on the bottom in standard colours. Only cell types with at least one cell labelled are displayed. n = 329 cells from Vipr2-IRES2-cre/wt;Ai14/wt; n = 38 cells from Vipr2-IRES2-cre/wt;Slc32a1-T2A-FlpO/wt;Ai65/wt. c-f, Representative images of immunohistochemistry results; each image is representative of n = 2 experimental animals with stated genotypes. High- magnification images show tdT labelling in black, anti-PVALB in green and anti-tdTomato in red. Tissue sections (100 μm) were stained with anti- PVALB, anti-dsRed (labels tdTomato), and DAPI. Images are maximum intensity projections of confocal z-stacks. Scale bars are in micrometres. In Vipr2-IRES2-cre/wt;Ai14/wt mice (b, grey bars), apart from the expected labelling of chandelier cells (Pvalb-Vipr2), many non-neuronal cells are labelled (especially, Astro-Aqp4 and SMC-Aoc3 types, panel c). d, To improve labelling specificity, we created and examined Vipr2-IRES2-cre/wt;Slc32a1-T2A-FlpO/wt;Ai65/wt mice. As expected, labelling was more specific, now confined to chandelier cells, basket cells and Meis2 interneurons (dark bars in b and morphologically identified types in d). Notably, the chandelier cells within VISp did not express PVALB protein (d, panel 1). e, Genetic intersection of Vipr2 and Pvalb expression labelled cells with chandelier morphology corresponding to Pvalb-Vipr2 in ALM. f, However, Vipr2-IRES2-cre/wt;Pvalb-T2A-FlpO/wt;Ai65/wt did not label chandelier cells in VISp, but PVALB+ cells of basket morphology. This unexpected labelling may reflect historical expression of Vipr2 in a subset of other Pvalb cells or low adult Vipr2 expression that is not detected by scRNA-seq. In VISp-containing sections, some chandelier cells are labelled, but are observed outside of VISp (f, panel 3). RSP, retrosplenial cortex.