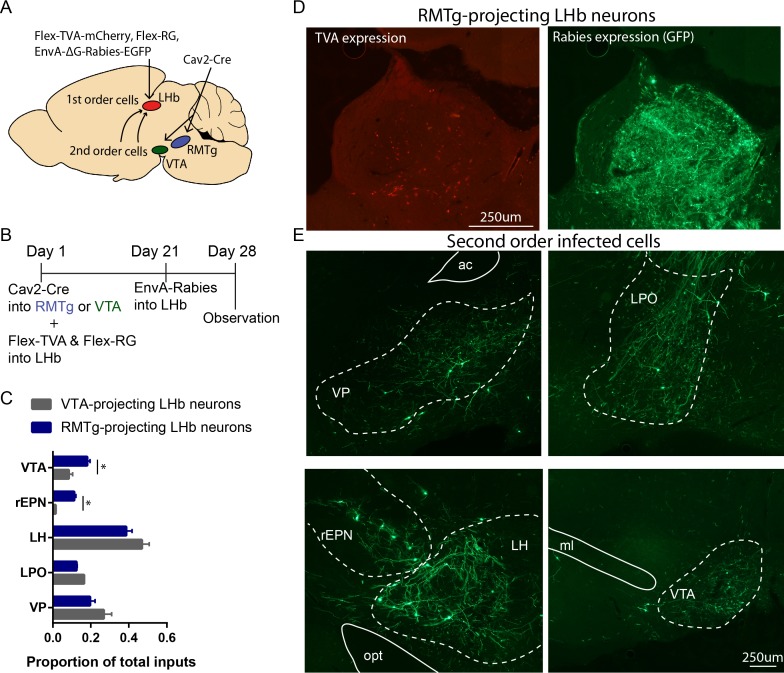
Figure 2. rEPN neurons innervate LHb neurons projecting to the RMTg.
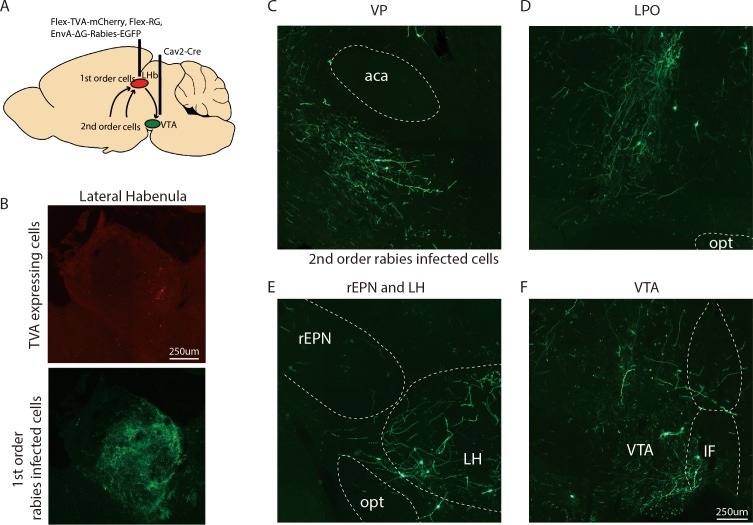
(A, B) Schematics of procedure in which retrogradely transported virus expressing Cre-recombinase was injected into the RMTg or VTA and viruses expressing flox-stopped TVA and RG were injected into the LHb. EnvA-ΔG-rabies virus was injected into the LHb 3 weeks later. Animals were perfused at the end of the forth week. (C) Neurons in the rEPN and the VTA preferentially projected to RMTg-projecting LHb neurons over VTA-projecting LHb neurons. (D) Representative pictures of RMTg-projecting TVA expressing cells and first-order rabies infected cells in the LHb. (E) Representative pictures of second-order rabies infected cells in the VP, LPO, rEPN, LH, and VTA after Cav2-Cre injection into RMTg, indicating neurons disynaptically connected to RMTg.