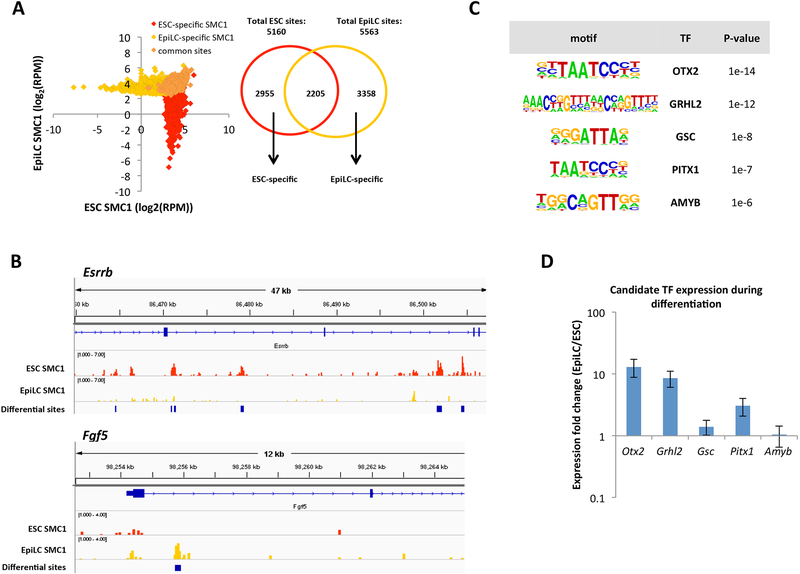
Figure 1. ChIP-seq for SMC1 identifies candidate TFs that regulate cohesin relocalization during the ESC to EpiLC transition.
A) Left: SMC1 signal at ESC-specific, EpiLC-specific, and common SMC1 sites called with MACS2 (FDR<0.05). To deplete insulators, sites co-bound by CTCF are not included. RPM = reads per million. Right: Venn diagram showing overlap of SMC1 sites in ESCs and EpiLCs. We identified 2955 ESC-specific, 3358 EpiLC-specific, and 2205 common SMC1 sites. B) SMC1 ChIP-seq tracks at Esrrb and Fgf5 genomic loci, with blue bars indicating significant differential peaks between ESCs and EpiLCs as called by MACS2. C) Top transcription factor motifs enriched at EpiLC-specific SMC1 sites, using all ESC SMC1 sites as a background. D) Expression fold change in EpiLCs vs ESCs for top 5 transcription factor candidates as quantified by qPCR. Error bars represent standard deviation of n=3 biological replicates. p <0.05 for OTX2 and GRHL2 by student t-test.