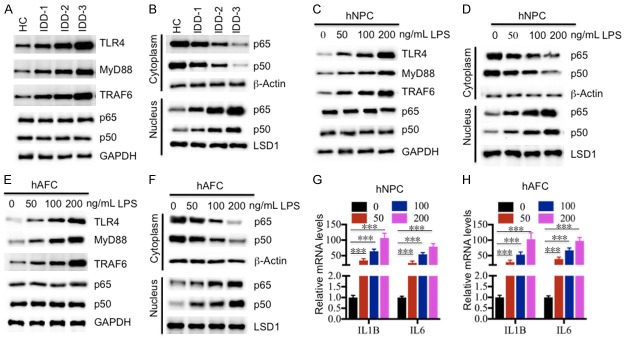
Figure 2.
Activation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. (A) The protein levels of members of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in IDD tissues. The protein levels of TLR4, MyD88, TRAF6, p65 and p50 were examined in a healthy control (HC), and three IDD tissues, including IDD-1, -2 and -3. GAPDH was used as the loading control. (B) Protein levels of p65 and p50 in the cytoplasm and nucleus. The cytoplasmic and nuclear portions of the IDD tissues were prepared, and immunoblots were performed to examine the p65 and p50 levels in these two portions. β-Actin and LSD1 were used as controls to determine the levels of cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins, respectively. (C and D) The protein levels of members of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in (C) hNPC and (D) hAFC cells treated with LPS. The hNPC and hAFC cells were treated with different concentrations of LPS (0, 50, 100 or 200 ng/mL) for 2 hr, followed by detecting the protein levels of TLR4, MyD88, TRAF6, p65 and p50. GAPDH was used as the loading control. (E and F) Protein levels of p65 and p50 in the cytoplasm and nucleus of (E) hNPC and (F) hAFC cells. The cytoplasmic and nuclear portions of cells used in (C) and (D) were prepared, and immunoblots were performed to examine the p65 and p50 levels in these two portions. β-Actin and LSD1 were used as controls to determine the levels of cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins, respectively. (G and H) The relative mRNA levels of IL1B and IL6 in (G) hNPC and (H) hAFC cells treated with LPS. Cells used in (C) and (D) were subjected to RNA isolation, followed by measuring the expression levels of IL1B and IL6 by qRT-PCR. ***P < 0.001.