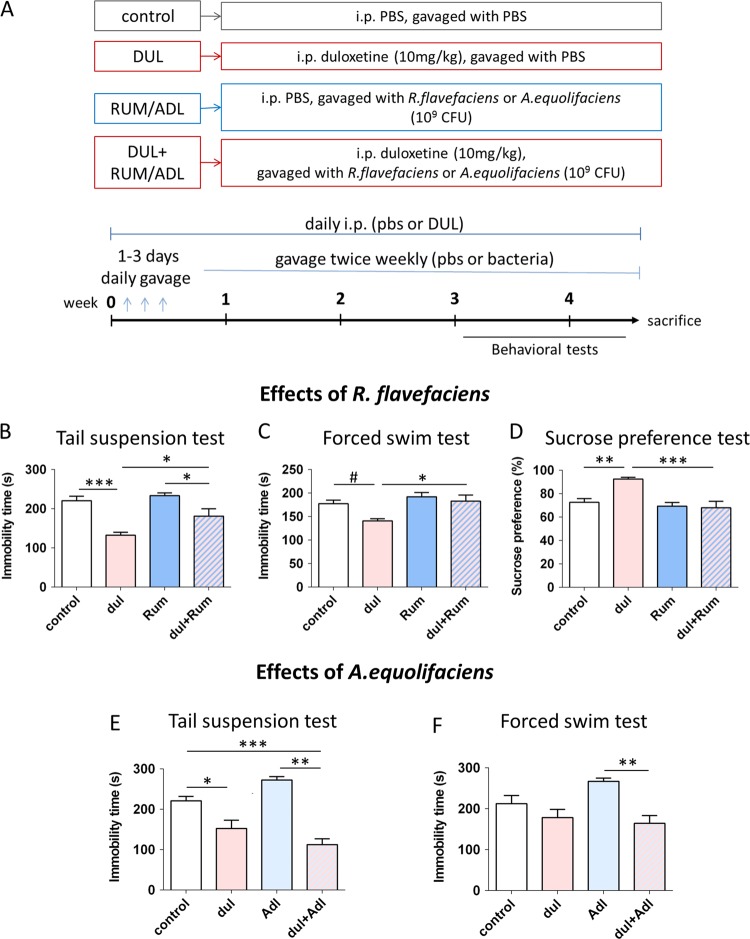
Fig. 3. R. flavefaciens, but not A. equolifaciens, abolished antidepressive effect of duloxetine.
a Experimental design of studies examining behavioral effects of duloxetine and bacterial treatments (R. flavefaciens or A. equolifaciens). Mice were chronically treated with antidepressant and/or bacteria, followed by behavioral testing. b–d Effects of duloxetine and R. flavefaciens on depressive-like behavior. R. flavefaciens supplementation abolished antidepressive effect of duloxetine in tail suspension test (b), forced swim test (c) and sucrose preference test (d). n = 10 (control), n = 10 (dul), n = 11 (Rum), n = 11 (dul+Rum), animals per group. e, f Effects of duloxetine and A. equolifaciens on depressive-like behavior. Duloxetine still reduced depressive-like behavior after A. equolifaciens treatment in tail suspension test (e) and forced swim test (f). n = 10 (control), n = 10 (dul), n = 11 (Adl), n = 10 (dul+Adl), animals per group. #0.1 > p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Tukey’s post hoc test; data represent mean ± SEM. dul duloxetine, Rum R. flavefaciens, Adl A. equolifaciens