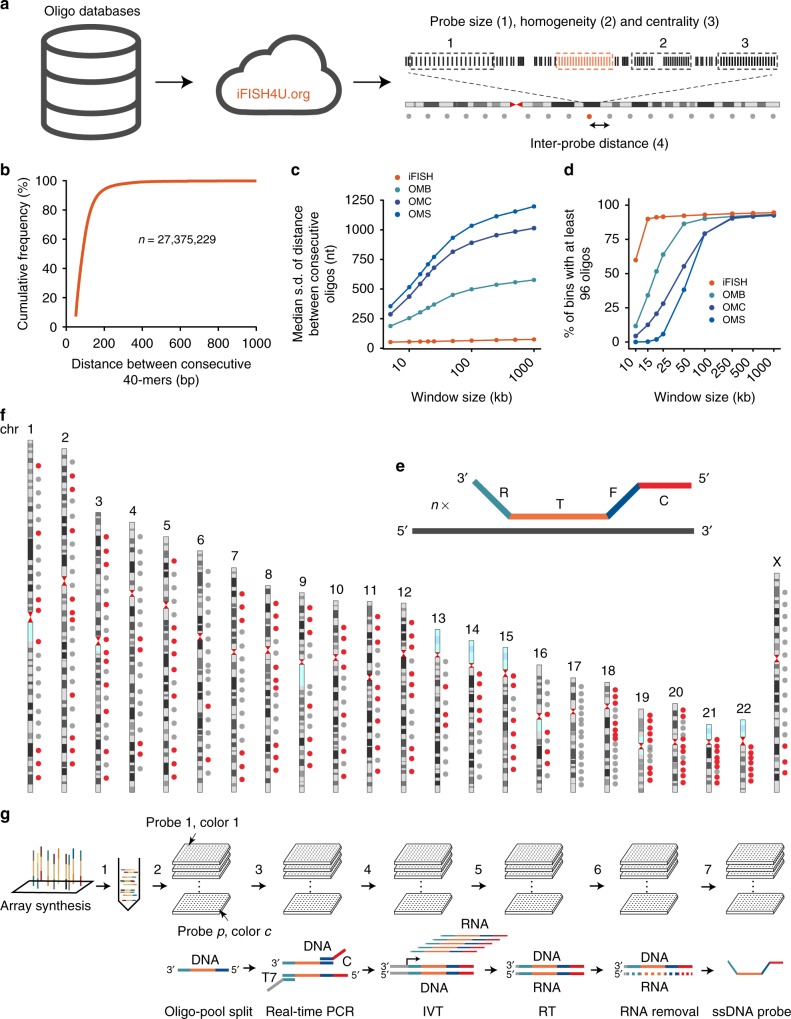
Fig. 1.
iFISH implementation. a Scheme of iFISH4U. Pre-designed genome-wide databases of oligos (left) are used as input by the iFISH4U web interface (center) to select oligos within one or more user-specified genomic regions, based on the indicated features. Features 1–3 are used while designing single probes, whereas all the four features are used to design multiple probes on the same chromosome. The black dashed boxes indicate examples of probes within the same region of interest, with the same number of oligos (vertical bars), but suboptimal size (1), homogeneity (2), or centrality (3), whereas the orange box represents the probe of choice having optimal size, homogeneity and centrality. b Cumulative distribution of the distances between consecutive oligos in the human 40-mers database. c Median standard deviation (s.d.) of the distance between consecutive oligos, inside non-overlapping genomic windows of the indicated size, in the 40-mers database and OligoMiner (OM) hg19 databases. OMB, OM ‘Balance’. OMC, OM ‘Coverage’. OMS, OM ‘Stringent’. d Percentage of non-overlapping genomic windows of the indicated size, containing at least 96 oligos, in the 40-mers database and OM hg19 databases. e Scheme of oligos in iFISH probes. Each probe consists of n oligos differing in the T sequence. f Location of the 330 iFISH probes targeting all the human autosomes and chrX. Red dots, individually tested probes (see Fig 2a, b). g Scheme of the pipeline used to produce iFISH probes. (1) Up to 12,000 oligos, corresponding to a maximum of 125 probes each containing 96 oligos, are synthesized on an array and then pooled together. (2) The oligo-pool is dispensed into n 96-well plates, depending on the total number of probes (p) and colors per probe (c). (3) In each well, the oligos corresponding to the same probe are selectively amplified using a probe-specific PCR primer pair that incorporates the T7 promoter sequence (T7) and color adapter sequence (C), and (4) successfully amplified probes are purified and linearly amplified by in vitro transcription (IVT). (5) Purified IVT products are reverse transcribed (RT), (6) RNA is hydrolyzed, and finally (7) single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) is purified to obtain ready-to-use probes