Fig. 6. The distance between hotspots I and II determines the perivascular crawling pattern upon stimulation with N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine.
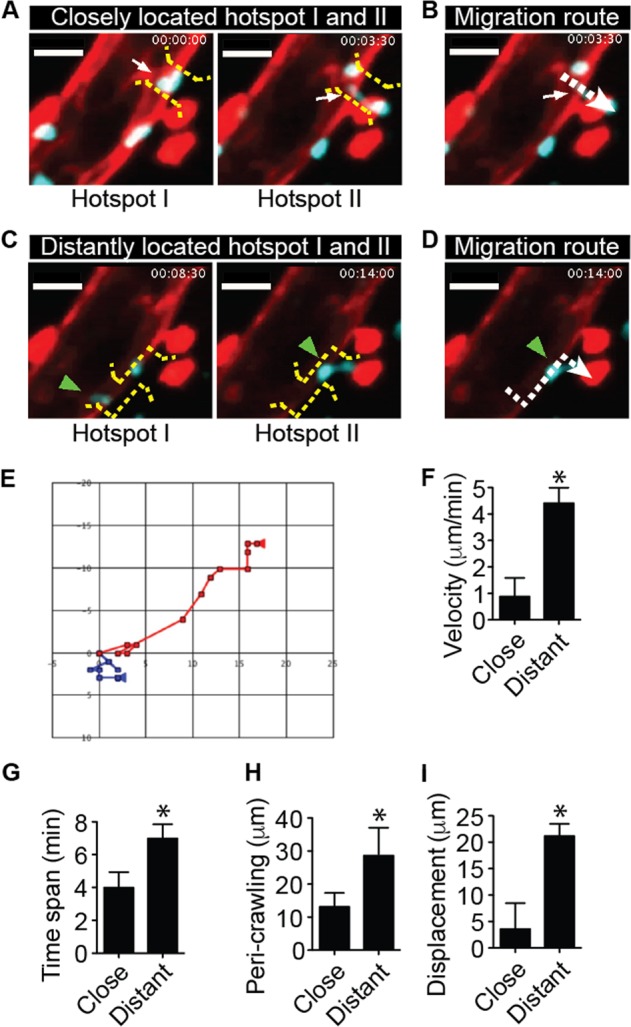
a The neutrophil quickly penetrated the vascular endothelium through closely located hotspots I and II. The white arrow indicates a hotpot, which is located between the yellow dotted brackets. b The migration route of the neutrophil through the closely located hotspots I and II is indicated by the white dotted arrow. c The neutrophil spent considerable time in the endothelial basement membrane when using the route of distantly located hotspots I and II. The green arrowhead indicates a hotpot between the yellow dotted brackets. d The migration route of the neutrophil through the distantly located hotspots I and II is indicated by the green arrowhead. a–d were generated from Video 12. Scale bar, 20 μm. e The migratory patterns of neutrophils using the quick route and round route during extravasation were compared in rectangular coordinates. Unit; μm. Velocity (f), time span (g), perivascular crawling distance (h), and displacement (i) were compared between fast penetrating and round penetrating neutrophils. *P < 0.005. A representative dataset from >10 extravasating neutrophils from 3 independent intravital imaging experiments is shown
