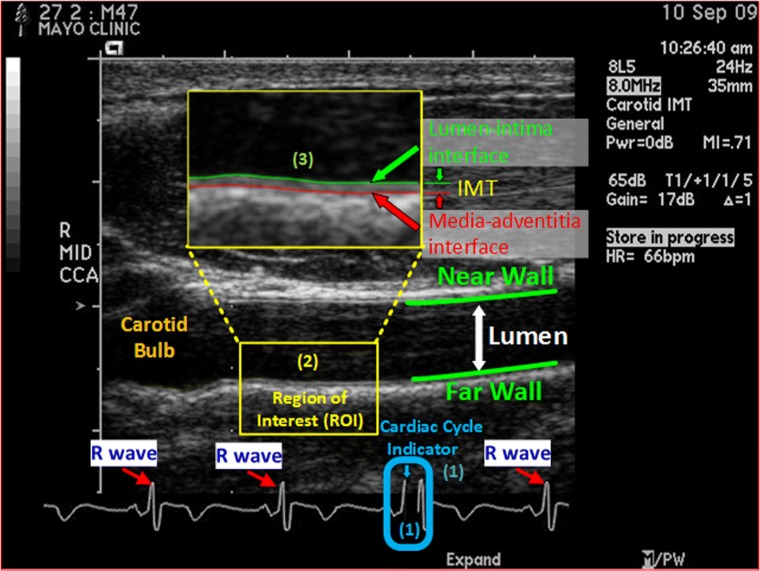
Fig. 1.
End-diastolic ultrasound frame (EUF), showing a longitudinal view of a common carotid artery in an ultrasound B-scan image. EUFs are selected based on the cardiac cycle indicator, a black line, which indicates to where in the cardiac cycle the current frame corresponds. CIMT is the distance between the lumen-intima interface (in green) and the media-adventitia interface (in red) at an EUF, and it is determined in a region of interest (ROI) approximately 1 cm distal from the carotid bulb at the EUF. In a CIMT exam, the sonographer examines the common carotid arteries on both sides of the neck from the two angles, yielding 4 CIMT ultrasound videos for each subject. Interpreting each CIMT video involves three manual steps: (1) select 3 EUFs in each video based on the cardiac cycle indicator; (2) localize an ROI in each selected EUF according to the carotid bulb; (3) trace the lumen-intima and the media-adventitia interfaces within the localized ROI and compute the minimum, maximum, and average of the distance between the traced lumen-intima and the media-adventitia interfaces. The final CIMT report of a subject is a statistical summary of all CIMT measurements on the 12 (4 × 3) EUFs from the 4 CIMT videos acquired for the subject. This figure is used with permission [28] under IEEE license number 4407260599014