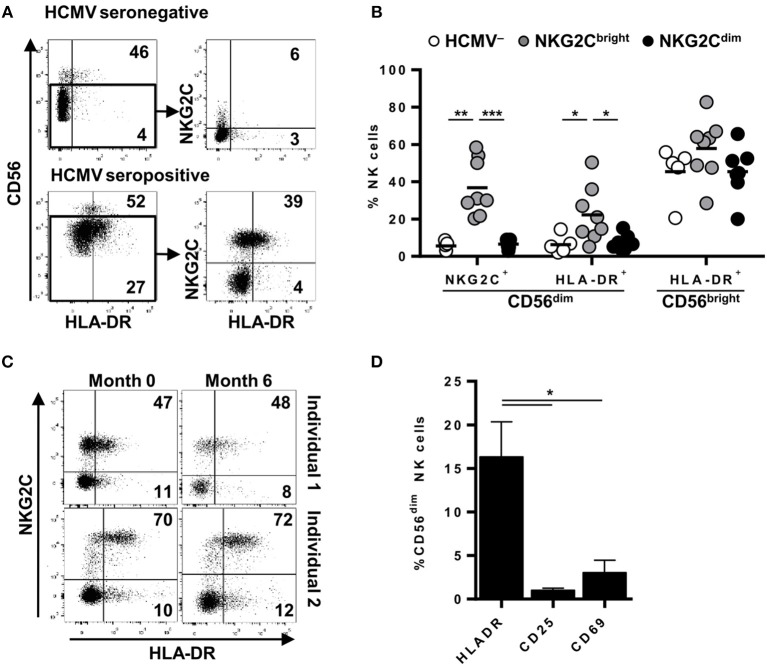
Figure 1.
Surface expression of HLA-DR is stably detected in variable proportions of circulating NKG2C+ adaptive NK cells in the absence of activation markers. NKG2C and HLA-DR expression was analyzed by flow cytometry in circulating NK cells from seronegative (n = 5; HCMV–) and seropositive (HCMV+) individuals with (n = 8; NKG2Cbright) or without (n = 7; NKG2Cdim) NKG2C+ adaptive NK cells. (A) Representative dot plots of NKG2C and HLA-DR expression in CD56dim NK cells from HCMV- and HCMV+ individuals. Inset numbers indicate proportions of HLA-DR+ in CD56bright and CD56dim gates. (B) Percentage of NKG2C+ and HLA-DR+ cells in CD56dim and CD56bright NK cell subsets in individuals categorized according to their HCMV serology and the presence (NKG2Cbright) or absence (NKG2Cdim) of NKG2C+ adaptive NK cells. (C) Dot plots showing NKG2C and HLA-DR phenotype along time in two out of five HCMV+ individuals analyzed. Inset numbers indicate frequencies of HLA-DR+ cells in NKG2C+ and NKG2C- NK cells. (D) HLA-DR, CD25, and CD69 expression on circulating CD56dim NK cells from HCMV+ individuals with NKG2C+ adaptive NK cells (mean ± SEM, n = 6) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).