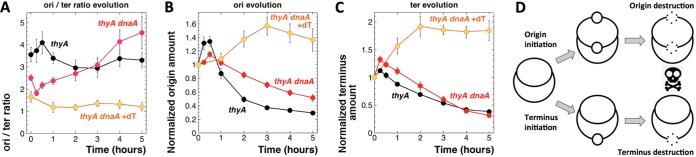
FIG 5.
Evolution of the origin and terminus quantities in the thyA and thyA dnaA601 cultures during T starvation at 42°C. The strains are as follows: thyA mutant, KKW58; thyA dnaA601(Ts) mutant, SRK291. (A) Evolution of the ori/ter ratios in the thyA –dT, thyA dnaA601(Ts) –dT, and dnaA thyA601(Ts) +dT cultures at 42°C. In the –dT cultures, dT was removed at time zero. Experimental conditions were as described for Fig. 4B. (B and C) Evolution of the origin (B) and terminus (C) amounts in the cultures and conditions described for panel A. (D) Model of the chromosomal behavior during thymine starvation. All chromosomes initiate, but some do it in the origin, while others do it in the terminus. As a result of thymine limitation, both types of nascent bubbles become vulnerable to degradation, opening irreparable double-strand gaps in the chromosome.