FIG 2.
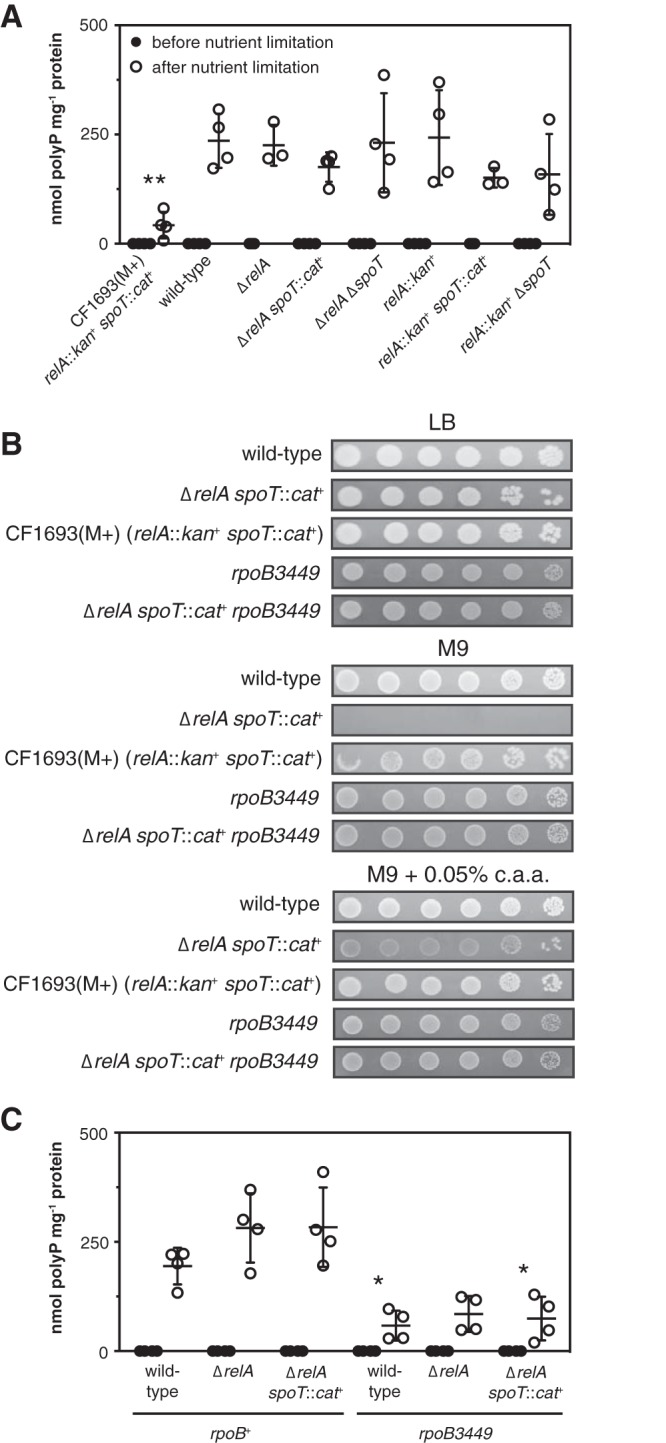
Stringent alleles of RNA polymerase can reduce polyP synthesis. (A) E. coli CF1693(M+) (ϕ80+ λ+ relA251::kan+ spoT205::cat+ rpoB1693 rpoD1693), wild-type MG1655, and isogenic MG1655 ΔrelA782, ΔrelA782 spoT207::cat+, ΔrelA782 ΔspoT1000, relA251::kan+, relA251::kan+ spoT205::cat+, and relA251::kan+ ΔspoT1000 strains were grown to an A600 of 0.2 to 0.4 in LB and then shifted to minimal medium for 2 h (n = 3 or 4; means ± SD are shown). (B) Overnight cultures of E. coli MG1655, CF1693(M+), and MG1655 isogenic ΔrelA782 spoT207::cat+, rpoB3449, and ΔrelA782 spoT207::cat+ rpoB3449 mutant strains were resuspended to an A600 of 1 in PBS, serially diluted and spotted on LB, M9 glucose, or M9 glucose plates containing 0.5 g liter−1 Casamino Acids (c.a.a.), and incubated at 37°C. The results shown are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. (C) E. coli MG1655 wild-type and isogenic ΔrelA782, ΔrelA782 spoT207::cat+, rpoB3449, ΔrelA782 rpoB3449, and ΔrelA782 spoT207::cat+ rpoB3449 strains were grown at 37°C to an A600 of 0.2 to 0.4 in rich medium (LB) (black circles) and then shifted to minimal medium (MOPS with no amino acids, 4 g liter−1 glucose, and 0.1 mM K2HPO4) for 2 h (white circles) (n = 4; means ± SD are shown). polyP concentrations are in terms of individual phosphate monomers. Asterisks indicate polyP levels significantly different from those of the wild type (rpoB+) for a given experiment (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple-comparison test; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).
