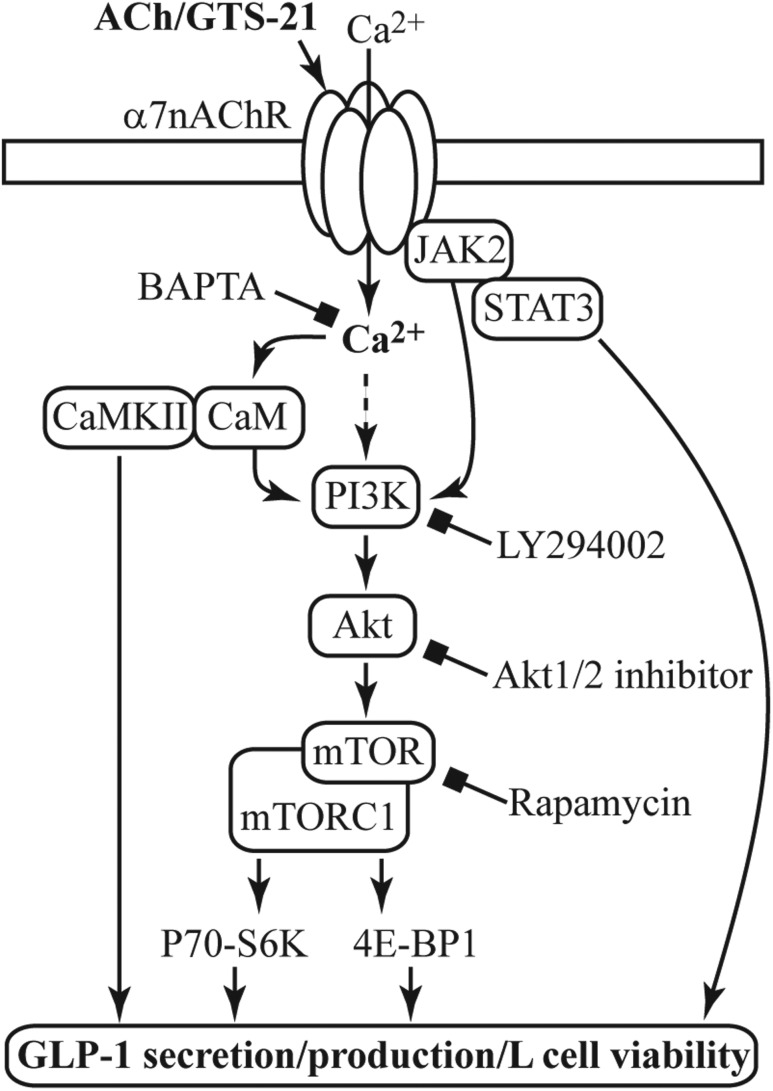
Figure 9.
A model for α7nAChR coupling to L-cell function, growth, and survival. Acetylcholine (ACh) or GTS-21 activates α7nAChR and promotes Ca2+ influx. Activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway downstream of α7nAChR is involved in regulating GLP-1 secretion and cell viability, as revealed by the use of LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor), Akt1/2 kinase inhibitor, or rapamycin (mTOR inhibitor). Coupling of α7nAChR to PI3K activation can occur through several pathways including Ca2+-calmodulin (CaM) (41) and Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) (42). Ca2+ can also promote GLP-1 secretion directly or through Ca2+/calmodulin‒dependent kinase II (CaMKII) (43). The Ca2+ chelator BAPTA-AM inhibits all depicted effects of GST-21. Numerous downstream effectors of the metabolically regulated mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) (44) are involved in cell viability, and determining which pathways are important to L-cell biology requires further investigation.