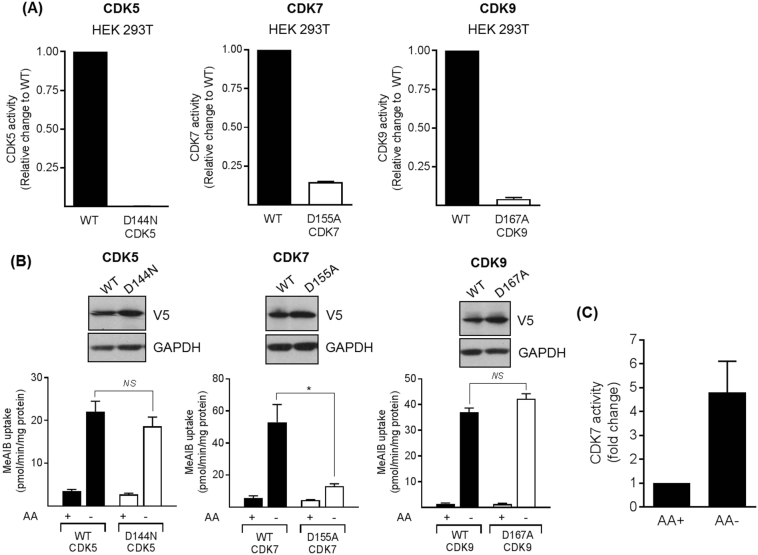
Fig. 6.
Effects of overexpressing wild-type and dominant interfering mutants of CDK5, CDK7 and CDK9 upon System A adaptation and effects on AA withdrawal (AA-) on CDK7 activity in HEK293T cells.
(A) HEK293T cells were transfected with 5 μg of the following vectors; pShuttleCMV/CDK5-WT, pShuttleCMV/CDK5-D144N, pShuttleCMV/p35-FLAG, pShuttleCMV/CDK7-WT, pShuttleCMV/CDK7-D155A, pShuttleCMV/CDK9-WT and pShuttleCMV/CDK9-D167A as indicated. Cell lysates were prepared and the over-expressed CDKs immunoprecipitated from either 500 μg (CDK5) or 1 mg (CDK7 and CDK9) lysate using antibody targeted to the V5 tag. Activity assays for CDK5, CDK7 and CDK9 were carried out. Data is expressed as a relative change to the wild type kinase activity. (B) Cells were transduced with adenovirus expressing either V5 tagged WT or DN forms of CDK5 (D144N), CDK7 (D155A) and CDK9 (D167A). 24 h post transfection cells were incubated in the presence/absence of amino acids for 6 h prior to assaying Me-AIB uptake or (C) analysis of CDK7 activity in V5 immunoprecipitates. Data in all cases is presented as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3). Blots are representative of at least three independent experiments. NS, not significant