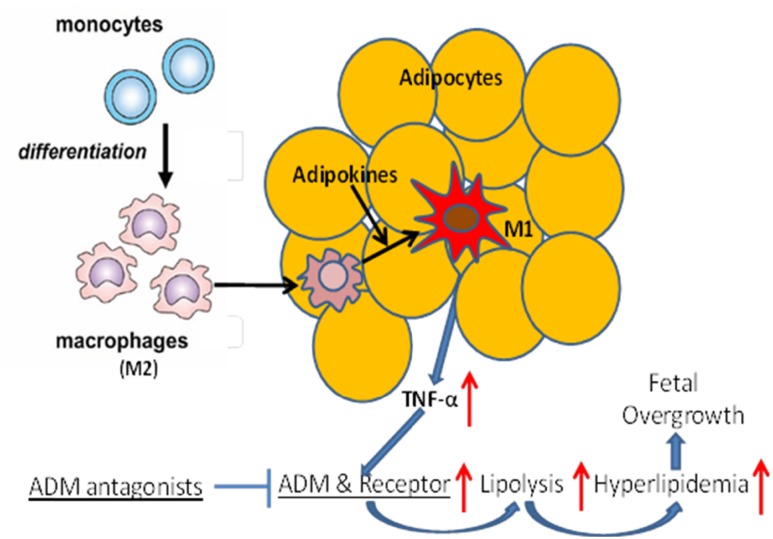
Figure 6.
Schematic illustration of ADM action in human adipose tissue. Monocyte-differentiated macrophages (M2) migrate into adipose tissue. Local factors, such as adipokines, activate anti-inflammatory M2 to proinflammatory M1 and produce increasing amounts of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, which stimulate expression of ADM and its receptors in adipose tissue, leading to maternal lipolytic status, hyperlipidemia, and fetal overgrowth. Blockade of ADM actions could improve the ADM-related lipid dysregulation seen in GDM.